This calculator automates the computation of the Rank Sum Test. It’s particularly useful in scenarios where the data does not meet the normality assumption required by other tests like the t-test. By inputting sample data, users can quickly determine if there is a significant difference between two groups.
Formula of Rank Sum Test Calculator
The core of the Rank Sum Test Calculator is based on the formula:
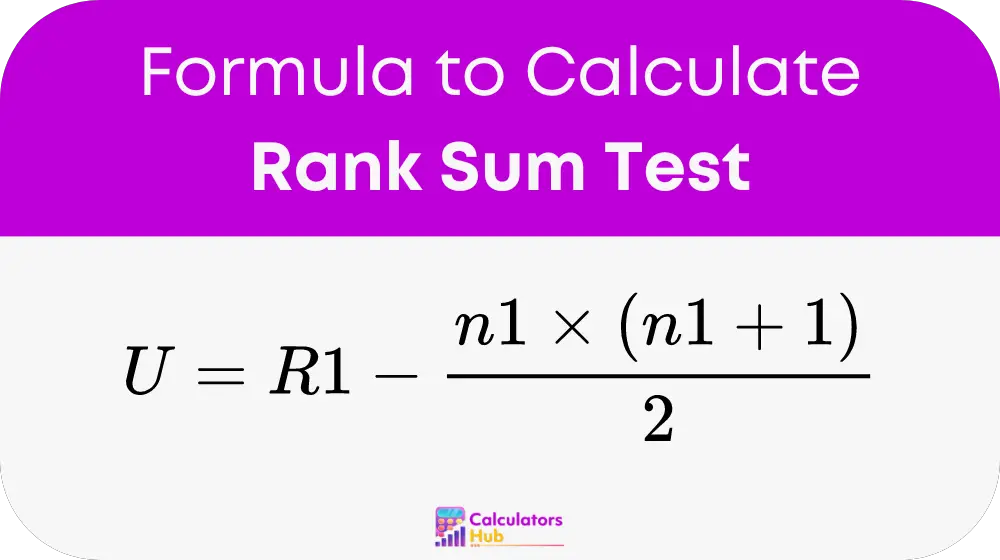
where:
- U is the test statistic,
- R1 represents the sum of the ranks in the first sample,
- n1 is the size of the first sample.
To compute R1, all observations from both samples are ranked together. The ranks corresponding to the first sample are then sum to obtain R1. After computing U, its value is compared against critical values from the Wilcoxon rank-sum distribution to assess statistical significance.
Helpful Table for Common Statistical Terms
Understanding common statistical terms is crucial for using the Rank Sum Test effectively. Here’s a table defining essential terms and providing critical values necessary for interpretation:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| U | Test statistic used in the Rank Sum Test |
| R1 | Sum of ranks in the first sample |
| n1 | Size of the first sample |
| Critical Value | Threshold value to determine significance |
Example of Rank Sum Test Calculator
Consider a study comparing the effectiveness of two medications. Using the Rank Sum Test, we can determine if there is a significant difference in efficacy between the two groups. By entering the ranks and sizes of each group into the calculator, it computes the U statistic and compares it to the critical values to provide a clear, interpretable result.
Most Common FAQs
The Rank Sum Test does not require the data to follow a normal distribution, unlike the t-test, making it more versatile for non-normal data.
A U statistic lower than the critical value indicates a significant difference between the two samples.
Yes, it is suitable for both small and large sample sizes, providing flexibility in various research scenarios.