The Molar Heat Capacity Calculator is designed to compute the heat capacity of a substance per mole at a constant volume or pressure. This measure, crucial in thermodynamics, helps predict the energy needed to raise the temperature of a mole of substance by one degree Kelvin. The calculator automates these calculations, providing quick and accurate results.
Formula of Molar Heat Capacity Calculator
The foundational formula used in the Molar Heat Capacity Calculator is straightforward:
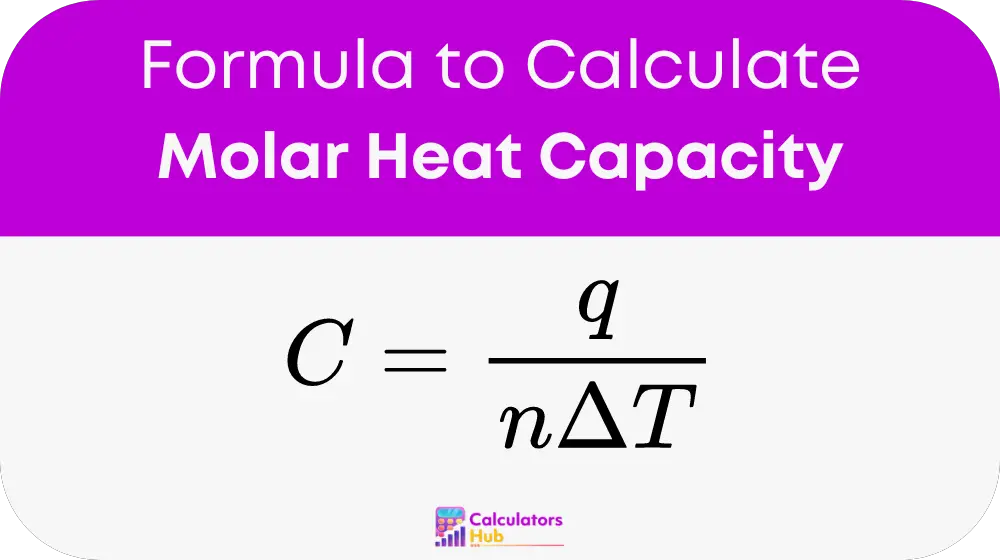
Where:
- C represents the molar heat capacity (in Joules per mole Kelvin),
- q is the heat energy transferred (in Joules),
- n is the amount of substance (in moles),
- delta T is the temperature change (in Kelvin).
Understanding each component of this formula is essential for anyone looking to utilize the calculator effectively.
Helpful Table for Common Terms and Conversions
To further aid our users, here is a table of common thermodynamic terms and their typical values or conversions, facilitating easier reference without the need for manual calculations:
| Term | Definition | Typical Value/Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Capacity | Energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree. | Varies by substance |
| Specific Heat | Heat capacity per unit mass. | J/(kg*K) |
| Molar Mass | Mass of a mole of particles of a substance. | g/mol |
Example of Molar Heat Capacity Calculator
Let’s consider an example to demonstrate the use of our calculator. Suppose you need to find the molar heat capacity of a substance where 500 Joules of heat is apply to 2 moles of the substance, causing a temperature increase of 5 K:
- C = 500 / (2 * 5) = 50 J/(mol*K)
Most Common FAQs
Molar heat capacity is the heat capacity per mole of substance, while specific heat is per unit mass.
Yes, it can be use for any substance as long as the necessary variables are known.