The Atmospheric Pressure Ratio Calculator computes the ratio of atmospheric pressure at a specified altitude to the standard atmospheric pressure at sea level. This ratio is critical for determining how atmospheric conditions affect various phenomena, from weather patterns to the performance of aircraft and the behavior of gases.
Formula of Atmospheric Pressure Ratio Calculator
The formula employed by the Atmospheric Pressure Ratio Calculator is based on the barometric formula, which is modified to calculate pressure ratios:
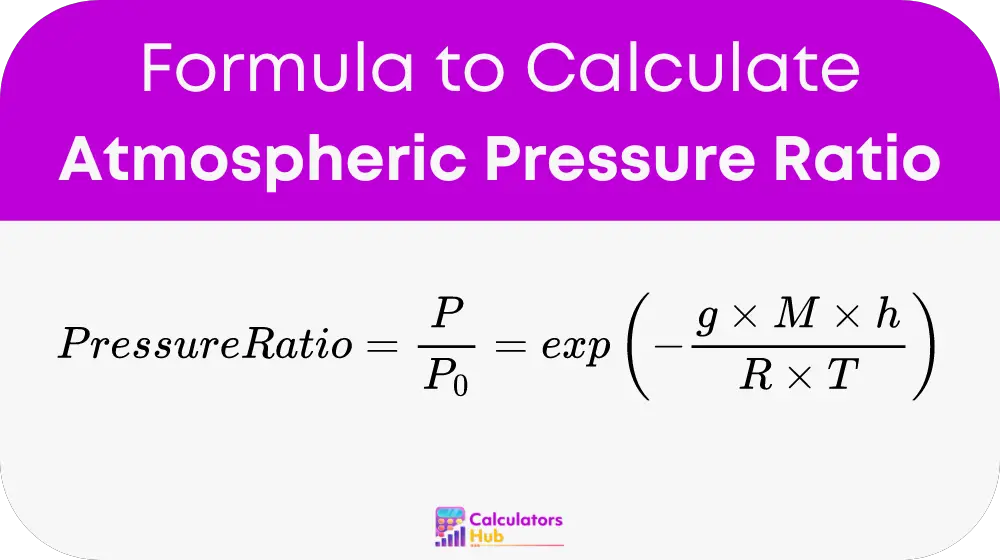
Where:
- P is the atmospheric pressure at the given altitude (Pascals).
- P0 is the standard atmospheric pressure at sea level (101325 Pascals).
- g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.80665 m/s²).
- M is the molar mass of Earth’s air (0.0289644 kg/mol).
- h is the altitude above sea level (meters).
- R is the universal gas constant (8.3144598 J/(mol·K)).
- T is the temperature in Kelvin (K).
This formula provides a clear method to understand how pressure decreases with an increase in altitude, essential for accurate scientific and practical applications.
Table of General Terms
Here’s a table defining key terms related to atmospheric pressure calculations:
| Term | Definition | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Ratio | Ratio of atmospheric pressure at altitude to that at sea level | Calculated Value |
| P | Atmospheric pressure at given altitude (Pascals) | Variable |
| P0 | Standard atmospheric pressure at sea level (Pascals) | 101325 Pa |
| g | Acceleration due to gravity (m/s²) | 9.80665 m/s² |
| M | Molar mass of Earth’s air (kg/mol) | 0.0289644 kg/mol |
| h | Altitude above sea level (meters) | 1000 m, 5000 m |
| R | Universal gas constant (J/(mol·K)) | 8.3144598 J/(mol·K) |
| T | Temperature in Kelvin (K) | 288 K (15°C) |
Example of Atmospheric Pressure Ratio Calculator
For an example calculation, consider determining the pressure ratio at an altitude of 5000 meters, assuming a temperature of 288 Kelvin:
- Pressure Ratio = exp(-9.80665 * 0.0289644 * 5000 / (8.3144598 * 288))
Pressure Ratio ≈ 0.561
This example indicates that the atmospheric pressure at 5000 meters is about 56.1% of the pressure at sea level under the given conditions.
Most Common FAQs
A1: The atmospheric pressure ratio is crucial for predicting weather conditions, designing aircraft. Understanding climatic changes at different altitudes, and conducting high-altitude scientific research.
A2: Temperature significantly impacts the atmospheric pressure ratio. Higher temperatures generally increase the pressure ratio by expanding air volume, thus reducing density.
A3: Yes, this calculator can be used for extremely high altitudes. However, users should consider additional factors such as humidity and wind for comprehensive atmospheric analysis.