The Atmospheric Pressure Calculator calculates the atmospheric pressure at different altitudes using the barometric formula. This is essential for predicting weather patterns, planning flights, and conducting high-altitude scientific research. By inputting variables such as altitude and temperature, users can obtain accurate atmospheric pressure readings essential for their specific needs.
Formula of Atmospheric Pressure Calculator
The formula used by the Atmospheric Pressure Calculator is a derivation of the barometric formula, which is critical for understanding how atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude:
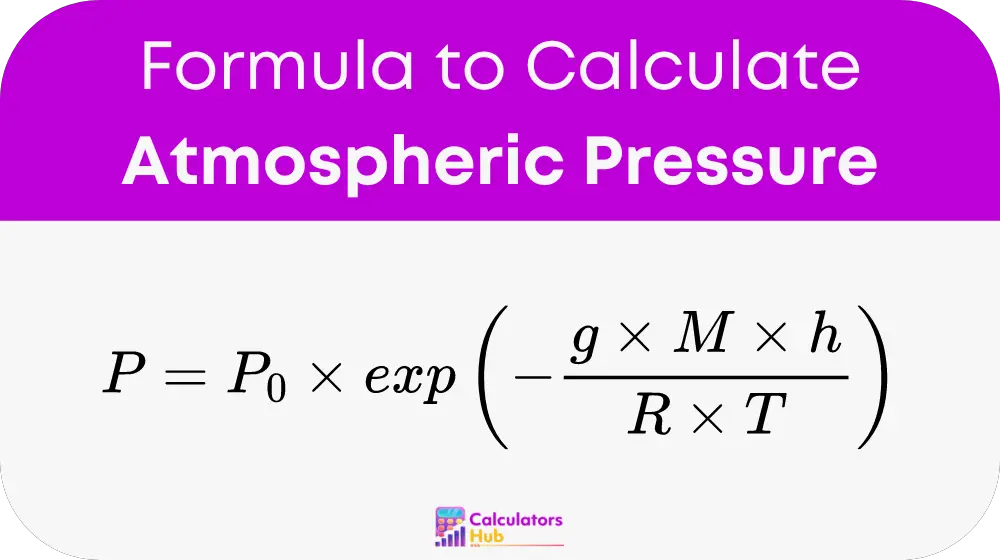
Where:
- P is the atmospheric pressure at the given altitude (Pascals).
- P0 is the standard atmospheric pressure at sea level (101325 Pascals).
- g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.80665 m/s²).
- M is the molar mass of Earth’s air (0.0289644 kg/mol).
- h is the altitude above sea level (meters).
- R is the universal gas constant (8.3144598 J/(mol·K)).
- T is the temperature in Kelvin (K).
This formula accurately models the decrease in atmospheric pressure as altitude increases, adjusting for temperature variations.
Table of General Terms
To enhance understanding, here’s a table defining key terms related to atmospheric pressure calculations:
| Term | Definition | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| P | Atmospheric pressure at the given altitude (Pascals) | Variable |
| P0 | Standard atmospheric pressure at sea level (Pascals) | 101325 Pa |
| g | Acceleration due to gravity (m/s²) | 9.80665 m/s² |
| M | Molar mass of Earth’s air (kg/mol) | 0.0289644 kg/mol |
| h | Altitude above sea level (meters) | 1000 m, 5000 m |
| R | Universal gas constant (J/(mol·K)) | 8.3144598 J/(mol·K) |
| T | Temperature in Kelvin (K) | 293 K, 310 K |
Example of Atmospheric Pressure Calculator
Consider a scenario where you need to calculate the atmospheric pressure at an altitude of 2000 meters, assuming a temperature of 293 K. Using the formula:
P = 101325 * exp(-9.80665 * 0.0289644 * 2000 / (8.3144598 * 293))
P ≈ 79577 Pa
This example shows that the atmospheric pressure at 2000 meters, with a temperature of 293 K, is approximately 79577 Pascals.
Most Common FAQs
A1: Calculating atmospheric pressure at various altitudes is essential for applications in aviation, meteorology, and mountainous activities, ensuring safety and operational efficiency.
A2: Temperature significantly affects atmospheric pressure; higher temperatures typically result in lower atmospheric pressures at a given altitude due to the expansion of air.
A3: Yes, the Atmospheric Pressure Calculator can be used for extreme altitudes, but it’s important to consider that extreme conditions might require additional adjustments for enhanced accuracy, such as incorporating humidity factors.