A CMRR (Common-Mode Rejection Ratio) calculator is a tool used in electronics and signal processing to determine the ability of a differential amplifier to reject common-mode signals. Common-mode signals are identical voltages present on both input terminals of an amplifier. By calculating the CMRR, engineers can evaluate an amplifier’s performance in minimizing noise or interference that affects both inputs equally.
The CMRR calculator is commonly used in the design, analysis, and troubleshooting of electronic circuits, particularly in audio systems, instrumentation amplifiers, and data acquisition systems. It helps ensure signal clarity and integrity by providing a quantitative measure of an amplifier’s efficiency in differentiating between useful signals and unwanted noise.
Formula of CMRR Calculator
The formula for calculating CMRR is as follows:
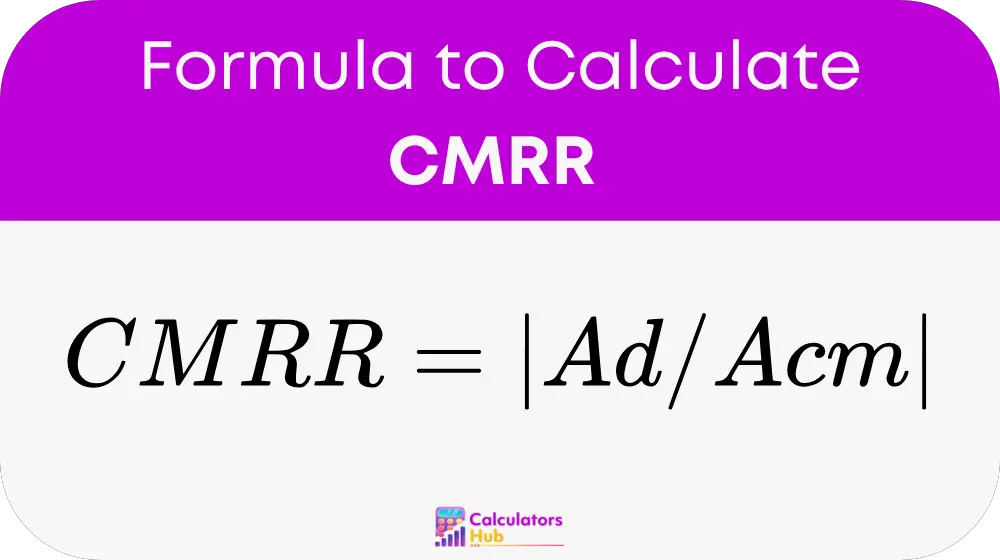
Where:
CMRR: Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
Ad: Differential Gain (gain for differential input signals)
Acm: Common-Mode Gain (gain for common-mode input signals)
The result is typically express in decibels (dB) using the formula:
CMRR (dB) = 20 × log10(CMRR)
This ratio helps engineers understand how well an amplifier suppresses noise or interference that is common to both input lines.
General Terms and Quick Reference Table
Here is a table that lists CMRR values and their corresponding decibel equivalents for common scenarios. This can be helpful for quick reference without the need for calculations:
| CMRR Ratio | CMRR (dB) | Amplifier Quality Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 dB | Poor |
| 100 | 40 dB | Average |
| 1,000 | 60 dB | Good |
| 10,000 | 80 dB | Excellent |
| 100,000 | 100 dB | High Precision |
In addition, many CMRR calculators include converters for quickly calculating gain values or decibel equivalents.
Example of CMRR Calculator
Let’s consider an example where an amplifier has a differential gain (Ad) of 10,000 and a common-mode gain (Acm) of 1. Using the formula:
CMRR = |10,000 / 1|
CMRR = 10,000
To express this in decibels:
CMRR (dB) = 20 × 4
CMRR (dB) = 80 dB
This means the amplifier has an excellent ability to reject common-mode signals, making it highly effective for reducing noise in the system.
Most Common FAQs
A high CMRR indicates that an amplifier can effectively suppress noise and interference common to both input terminals. This is essential in ensuring the accuracy and clarity of the output signal, especially in sensitive applications like medical instruments or communication systems.
CMRR is measure by applying a common-mode signal to both inputs of the amplifier and comparing the output with the differential gain. Specialize equipment or software-based tools are often use to ensure precise measurements.
An amplifier with a low CMRR will struggle to reject common-mode noise, resulting in a distorted or noisy output signal. This can lead to reduced performance in applications where signal integrity is critical.