The Aircraft Range Calculator is an essential tool in aviation used for planning and optimizing flight routes. This sophisticated calculator helps pilots and flight planners determine the maximum distance an aircraft can travel under specific conditions without needing to refuel. By integrating various flight parameters, the calculator ensures that flight plans are both efficient and safe, adhering strictly to aviation regulations and fuel management protocols.
Formula of Aircraft Range Calculator
The fundamental formula used in the Aircraft Range Calculator is:
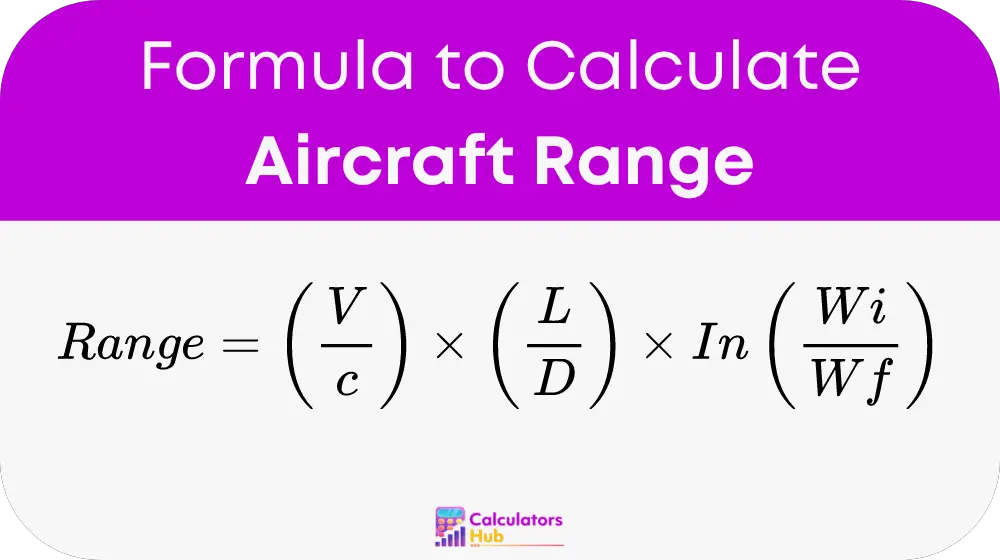
This formula encapsulates several critical factors:
- Range: The distance the aircraft can travel, measured in nautical miles or kilometers.
- V: The velocity of the aircraft, typically in meters per second or feet per second.
- c: The specific fuel consumption, which can be in kilograms per Newton-second or pounds per pound-force-hour.
- L/D: The lift-to-drag ratio, a crucial factor in determining the aircraft's efficiency.
- ln: Represents the natural logarithm.
- Wi: The initial weight of the aircraft, including fuel, cargo, and passengers, measured in kilograms or pounds.
- Wf: The final weight of the aircraft after fuel has been consumed, measured in kilograms or pounds.
This calculation allows for precise planning and can be crucial in determining the most efficient flight paths, particularly over long distances.
Table for General Terms
To aid in understanding and using the Aircraft Range Calculator, the following table provides a quick reference for common aviation terms related to aircraft performance:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Range | The maximum distance an aircraft can travel on a single fuel load. |
| Velocity (V) | Speed of the aircraft in the direction of flight. |
| Specific Fuel Consumption (c) | Fuel efficiency during operation at a given power setting. |
| Lift-to-Drag Ratio (L/D) | The efficiency of the aircraft's aerodynamic profile. |
| Initial Weight (Wi) | Total weight of the aircraft before the flight begins. |
| Final Weight (Wf) | Weight of the aircraft after fuel consumption. |
Example of Aircraft Range Calculator
Consider a scenario where an aircraft needs to calculate its range for a planned trip. Using the formula provided:
- If the aircraft travels at 250 meters per second,
- Has a specific fuel consumption of 0.85 kg/N-s,
- A lift-to-drag ratio of 15,
- An initial weight of 70,000 kg,
- And a final weight of 50,000 kg,
The range can be calculated as follows: Range = (250 / 0.85) * 15 * ln(70,000 / 50,000)
Most Common FAQs
The lift-to-drag ratio (L/D) is crucial as it determines the aerodynamic efficiency of the aircraft, impacting fuel consumption and range.
Pilots can increase their aircraft's range by optimizing the flight speed, managing weight, and planning efficient routes to reduce fuel consumption.
Yes, it is adaptable to a variety of flight types and conditions, providing essential calculations for both commercial and private flights.