The Claimed Hypothesis Mean Calculator is a specialized tool that helps users quickly determine the mean value of a dataset based on a claimed hypothesis. This calculator is particularly useful in scenarios where researchers need to compare a hypothesized mean to an observed sample mean to draw conclusions or further statistical inference.
Formula of Claimed Hypothesis Mean Calculator
The formula used by the Claimed Hypothesis Mean Calculator is straightforward:
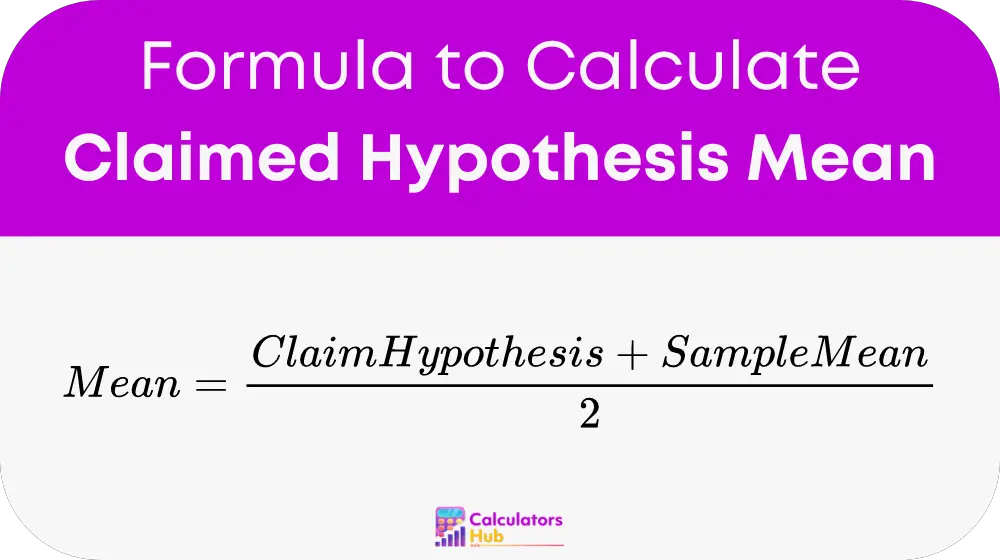
This formula calculates the average of the claimed hypothesis value and the sample mean. The claimed hypothesis is the theoretical mean which researchers believe the data should follow, while the sample mean is the actual average calculated from the collected data. Averaging these two gives a balanced mean that considers both the theoretical expectation and the empirical evidence.
Utility Table
To enhance the practicality of the Claimed Hypothesis Mean Calculator, here is a table of commonly calculated values:
| Claimed Hypothesis | Sample Mean | Calculated Mean |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 52 | 51 |
| 100 | 110 | 105 |
| 200 | 210 | 205 |
This table helps users visualize how different pairs of hypothesis and sample means interact to produce a final calculated mean, simplifying their tasks without the need for manual calculations.
Example of Claimed Hypothesis Mean Calculator
Consider a scenario where a psychologist claims that the average IQ of a group undergoing specific training is 110. After testing 30 participants, the observed sample mean IQ is 112. Using our calculator:
mean = (110 + 112) / 2 = 111
This example demonstrates how the calculator can be used to find a middle ground between the expected and observed averages, facilitating further analysis.
Most Common FAQs
A1: Yes, the calculator is versatile but is best used with continuous data where mean values are a relevant measure.
A2: No, there is no specific limit to the sample size; however, larger samples generally provide more reliable results.