The FIP Calculator measures a pitcher's effectiveness based solely on plays a pitcher can control: strikeouts, unintentional walks, hit by pitches, and home runs allowed. It removes the influence of team defense and luck on balls in play. By focusing on these core outcomes, FIP gives a clearer picture of a pitcher's true skill and helps compare pitchers fairly across teams and seasons.
The calculator falls under the Baseball Analytics & Advanced Pitching Stats category.
Formula of Fip (Fielding Independent Pitching) Calculator
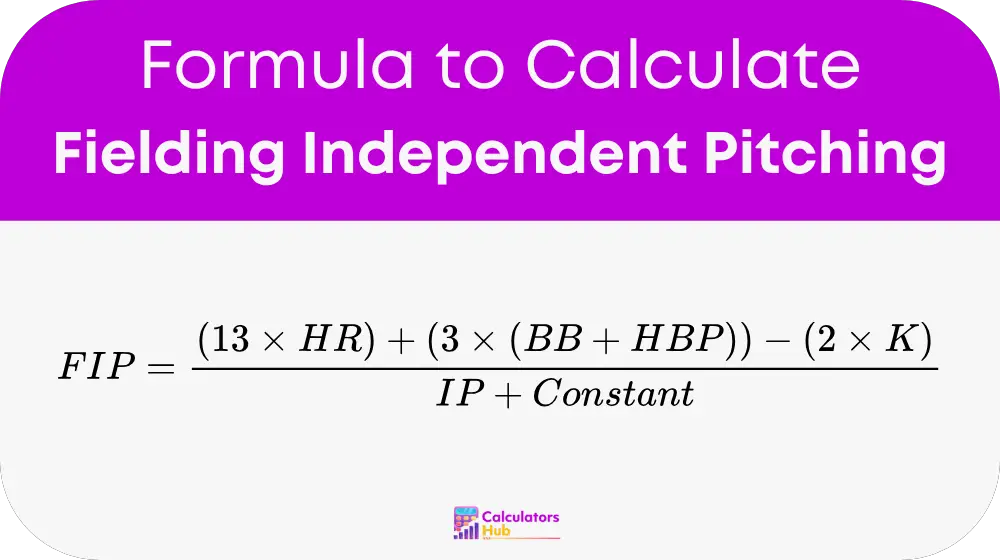
Where:
- HR = Home Runs allowed
- BB = Walks allowed (Base on Balls)
- HBP = Hit By Pitch
- K = Strikeouts
- IP = Innings Pitched
- Constant = League-specific number to scale FIP to the league average ERA
FIP League Constant Table
| League | Approx. Constant | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| MLB (Recent Average) | 3.10–3.20 | Varies by season |
| Minor Leagues | Check specific league stats | |
| Custom | Use actual league ERA minus calculated FIP without constant |
Tip: Always check official stats for up-to-date constants.
Example of Fip (Fielding Independent Pitching) Calculator
Scenario:
- Home Runs (HR): 15
- Walks (BB): 50
- Hit By Pitch (HBP): 5
- Strikeouts (K): 180
- Innings Pitched (IP): 200
- Constant: 3.1
Step-by-step:
- (13 × 15) = 195
- 3 × (50 + 5) = 3 × 55 = 165
- (2 × 180) = 360
- [195 + 165 − 360] / 200 = 0
- 0 + 3.1 = 3.1
Result:
The pitcher’s FIP is 3.10, matching league average — indicating solid, league-average independent performance.
Most Common FAQs
Generally, lower FIP means better pitching. A FIP below 3.00 is excellent, around 3.50 is good, and above 4.00 may signal average or below-average performance.
ERA (Earned Run Average) includes all earned runs, including those caused by errors or poor fielding. FIP ignores the effects of defense and luck, focusing only on results the pitcher controls directly.
Many analysts believe FIP better predicts future performance because it removes defensive variables. However, it’s best to consider both FIP and ERA, along with other stats like xFIP or SIERA, for a complete evaluation.