The True Position Calculator helps engineers and technicians determine the exact positional accuracy of a part or feature in a component. By calculating the true position, professionals can assess whether a part has been manufactured within the acceptable tolerances specified in the design. This is particularly important in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where precision is critical for safety and functionality.
Formula of True Position Calculator
The formula to calculate True Position is straightforward yet powerful:
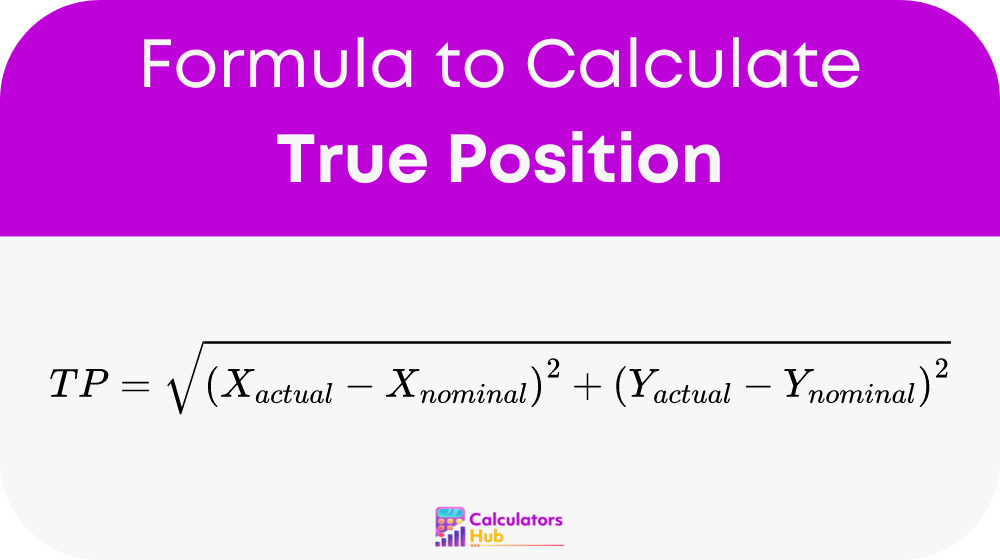
Here’s what each term represents:
- TP (True Position): The exact positional accuracy of the feature.
- X_actual and Y_actual: The measured coordinates of the feature on the manufactured part.
- X_nominal and Y_nominal: The intended coordinates of the feature according to the design specifications.
This formula computes the Euclidean distance between the actual measured position and the nominal designed position, providing a quantitative value of positional accuracy.
Practical Application Table
| True Position Value | Implication in Manufacturing |
|---|---|
| 0.01 mm | Extremely high precision; used in high-tech industries |
| 0.05 mm | Standard precision; suitable for automotive parts |
| 0.1 mm | Lower precision; acceptable in construction materials |
Additionally, the post will include a conversion table for units commonly used in different industries, facilitating the use of the True Position Calculator without the need for complex conversions.
Example of True Position Calculator
Consider a scenario where a component requires a hole drilled at a specific location. If the nominal position is (50, 50) mm, and the actual measured position of the hole is (50.05, 49.98) mm, the True Position would be calculated as follows: TP = sqrt((50.05 – 50)^2 + (49.98 – 50)^2) = sqrt(0.0025 + 0.0004) = sqrt(0.0029) ≈ 0.054 mm
This example shows the hole is within a very close tolerance, indicating high manufacturing precision.
Most Common FAQs
Common errors include incorrect measurements of actual positions and misunderstanding of nominal coordinates. It’s crucial to use precise measuring tools and clear design documents.
True Position directly affects the assembly fit, functionality, and compliance with industry standards. Precision in true position ensures that parts assemble correctly without modification and perform as intended.
Yes, there are several online calculators and software tools designed to automatically compute True Position from provided coordinates, significantly speeding up the process and reducing human error.