The Theoretical Acceleration Calculator helps users quickly determine the acceleration of an object when the net force applied and the mass of the object are known. This tool is crucial in both academic settings, where students can apply theoretical knowledge, and in real-world applications, such as engineering and mechanics, where precise calculations are necessary for designing and testing.
Formula of Theoretical Acceleration Calculator
To calculate acceleration, the calculator uses the formula:
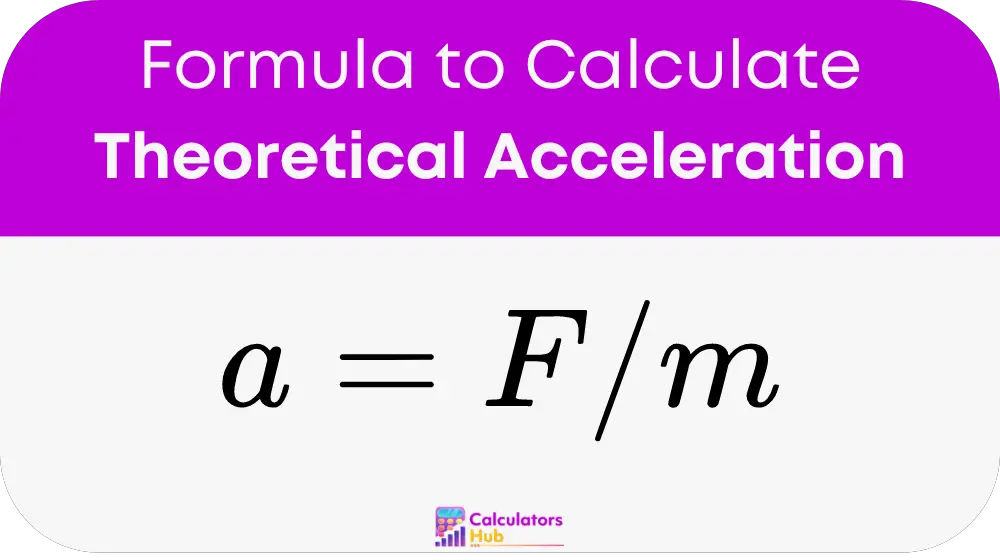
Where:
- a is the acceleration,
- F is the net force applied to the object,
- m is the mass of the object.
For accurate results, it is crucial to use the correct units:
- Force (F) should be in Newtons (N),
- Mass (m) should be in kilograms (kg),
- The resulting acceleration (a) will be in meters per second squared (m/s²).
Table of Common Terms
To assist users in making quick calculations without needing to perform them each time, here is a table of common terms with typical values for force and mass:
| Force (N) | Mass (kg) | Acceleration (m/s²) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 2 | 5 |
| 20 | 4 | 5 |
| 50 | 10 | 5 |
Example of Theoretical Acceleration Calculator
Consider a scenario where a force of 15 Newtons is applied to an object with a mass of 3 kilograms. Using the calculator:
a = 15 N / 3 kg = 5 m/s2
This example demonstrates how the calculator simplifies the process of determining acceleration.
Most Common FAQs
Always use Newtons (N) for force and kilograms (kg) for mass to ensure the acceleration is calculate in meters per second squared (m/s²).
The calculator interprets negative forces as the object moving in the opposite direction, but negative masses are not physically meaningful in classical mechanics.
Absolutely! It’s a great tool for teaching the principles of dynamics and helping students visualize the impact of different forces and masses on acceleration.