Velocity, a fundamental concept in physics, represents the speed of an object along with the direction of its movement. The magnitude of velocity, however, discards the directional component and focuses solely on the speed element, providing a scalar quantity which is of prime importance in various fields such as engineering, physics, and automotive industry. A Magnitude of Velocity Calculator simplifies the process of determining this scalar from the vector values of velocity, which can be complex depending on the motion’s dimensionality.
Formula of Magnitude of Velocity Calculator
One-Dimensional Motion:
In scenarios where movement is restricted to a straight line—either forward or backward—the calculation of magnitude of velocity is straightforward.
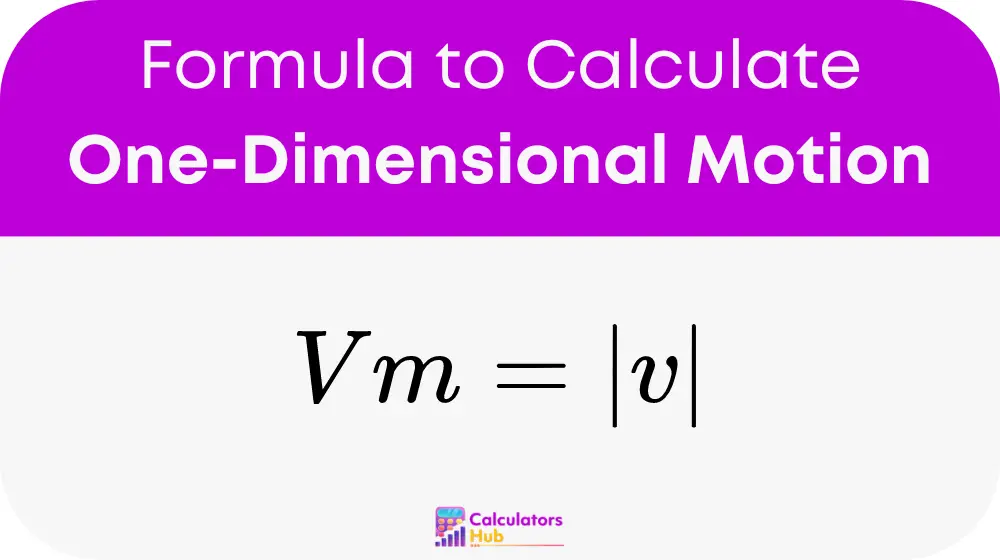
Where:
- Vm is the magnitude of velocity, with units typically in meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h).
- v represents the velocity which can be positive or negative depending on the direction.
Two-Dimensional Motion:
For motion that involves two-dimensional spaces, such as a projectile motion or vehicular movement in an area, the calculation incorporates both horizontal and vertical components.

Where:
- Vm is the magnitude of velocity.
- Vx and Vy are the horizontal and vertical components of velocity, respectively.
Tables for Quick Reference
To facilitate ease of use and quick calculations, the following table provides pre-calculated magnitudes of velocity for commonly encountered velocities in both one and two-dimensional motions:
| Velocity (v) or Components (Vx, Vy) | Magnitude of Velocity (Vm) |
|---|---|
| v = 20 m/s | 20 m/s |
| Vx = 3 m/s, Vy = 4 m/s | 5 m/s |
| v = -45 km/h | 45 km/h |
| Vx = 70 km/h, Vy = 70 km/h | 98.99 km/h |
This table acts as a quick reference to understand how magnitudes change with different velocities, especially useful for educational purposes and in practical scenarios where quick decision making is required.
Example of Magnitude of Velocity Calculator
Consider a car moving northeast at a speed of 50 km/h in a two-dimensional space where both x and y components of velocity are equally contributed:
- Vx=35.36 km/h
- Vy=35.36 km/h
Using the formula for two-dimensional motion:
Vm = √(35.36² + 35.36²) = √(2500) = 50 km/h
Thus, the magnitude of velocity of the car is 50 km/h, indicating its scalar speed irrespective of the direction.
Most Common FAQs
Speed is a scalar that refers only to how fast an object is moving, whereas the magnitude of velocity is the speed component of a vectorial velocity, ignoring its directional properties.
No, the magnitude of velocity, being a scalar quantity, is always a non-negative number. It represents the absolute value of velocity, which quantifies only the rate of movement.
For three-dimensional motion, involving Vx, Vy, and Vz as the respective velocity components along three mutually perpendicular axes, the magnitude is calculated as:
Vm = √(Vx² + Vy² + Vz²)
This provides a comprehensive scalar magnitude, taking into account all directional movements.