The Atmospheric Refraction Distance Calculator computes the additional distance that light or radio waves travel due to the bending of their path in the Earth’s atmosphere. This tool is indispensable for professionals and enthusiasts in navigation, surveying, and meteorology, who require accurate measurements adjusted for atmospheric conditions.
Formula of Atmospheric Refraction Distance Calculator
The formula used by the Atmospheric Refraction Distance Calculator is:
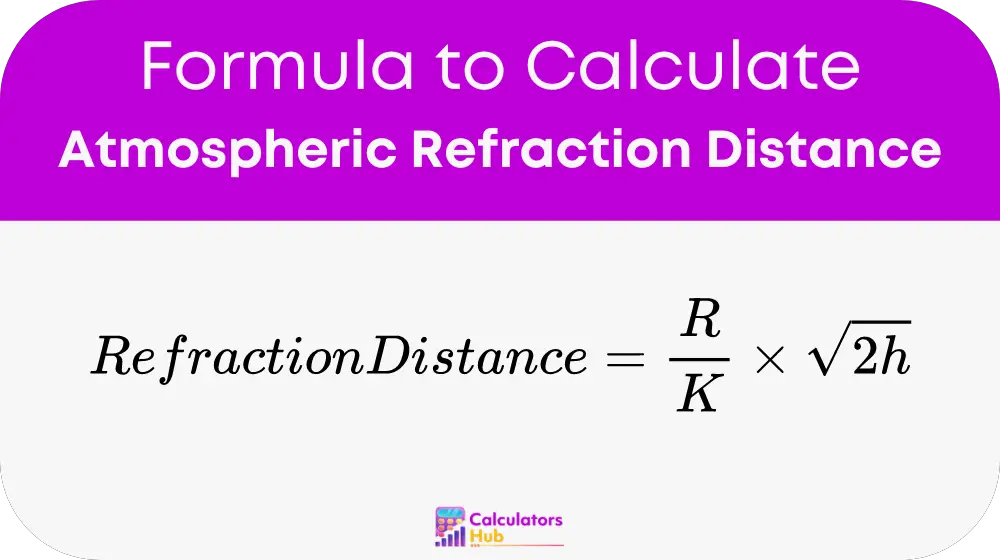
Where:
- R is the Radius of the Earth, approximately 6,371,000 meters.
- K is the refraction coefficient, typically around 0.13, but can vary depending on atmospheric conditions.
- h is the Height of the observer above the Earth’s surface in meters.
This formula allows users to determine how far beyond the horizon they can see or measure, given their height above the Earth’s surface, taking into account the bending of light by the atmosphere.
Table of General Terms
To aid understanding, here’s a table defining key terms related to atmospheric refraction distance calculations:
| Term | Definition | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| Refraction Distance | Additional distance light or radio waves travel due to atmospheric refraction | Calculated in meters |
| R | Radius of the Earth | 6,371,000 meters |
| K | Refraction coefficient, indicating the extent of atmospheric bending | 0.13 |
| h | Height of the observer above the Earth’s surface | 10 meters, 100 meters |
Example of Atmospheric Refraction Distance Calculator
For an example calculation, consider an observer who is 100 meters above the Earth’s surface, wanting to calculate the additional observable distance due to atmospheric refraction:
Refraction Distance = (6,371,000 / 0.13) * sqrt(2 * 100)
Refraction Distance ≈ 465,538 * 14.14 ≈ 6,582,837 meters
This example demonstrates that an observer at 100 meters height can see an additional approximately 6,582,837 meters due to atmospheric refraction, under standard conditions.
Most Common FAQs
A1: Calculating atmospheric refraction distance is critical for accurate observational data in astronomy, navigation, and surveying, ensuring that natural phenomena and measurements are accurately represented and accounted for.
A2: Atmospheric conditions such as temperature, pressure, and humidity can affect the refraction coefficient by altering the density and composition of the air, which in turn affects how much light bends.
A3: Yes, the calculator can be used at any altitude, but the accuracy might vary significantly with extreme altitudes where atmospheric conditions differ greatly from those at Earth’s surface.