The Air Pressure Speed Calculator is a vital instrument utilized in various engineering fields, such as aerospace, automotive, and environmental engineering. This tool calculates the speed of air flow resulting from differences in air pressure, essential for assessing system performance, designing ventilation systems, optimizing vehicle aerodynamics, and conducting environmental impact studies.
Formula of Air Pressure Speed Calculator
The speed of air flow can be determined using Bernoulli's equation, which relates the pressure difference to the air speed. This equation is crucial for understanding how changes in pressure affect air velocity:
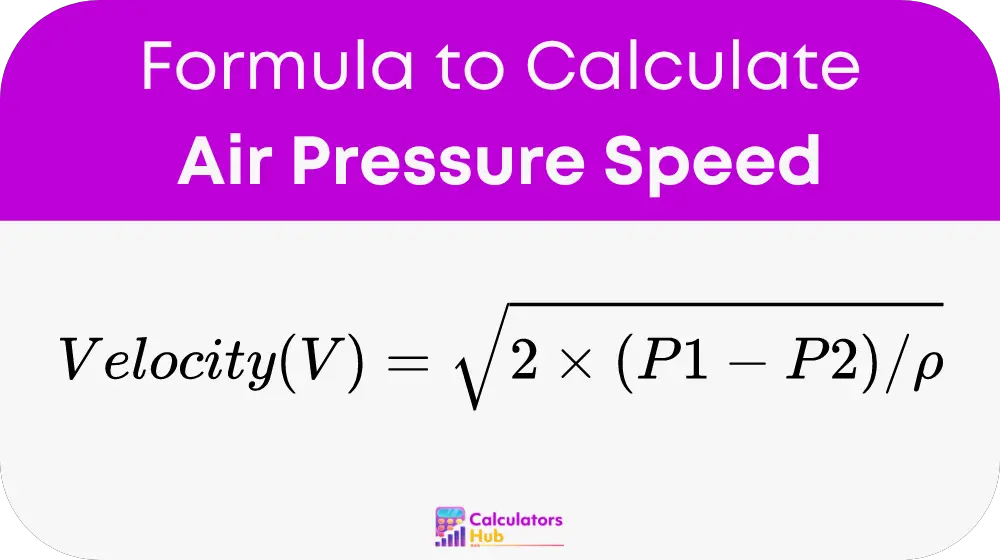
Explanation of Terms:
- V (Velocity): The speed at which air moves through a system, measured in meters per second (m/s).
- P1 (Total Pressure): The initial pressure in the system, measured in Pascals (Pa).
- P2 (Static Pressure): The pressure after changes within the system, also measured in Pascals (Pa).
- ρ (Air Density): The mass of air per unit volume, which affects how pressure differences convert to speed, measured in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³).
This formula provides a quick and reliable method for calculating air velocity, which is crucial for optimizing flow paths and ensuring efficient system operation.
General Terms Table
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Velocity (V) | The speed at which air is moving, typically in m/s. |
| Total Pressure (P1) | The pressure at the beginning of the system, in Pascals. |
| Static Pressure (P2) | The pressure after encountering resistance, in Pascals. |
| Air Density (ρ) | The density of the air, affecting how easily it moves, in kg/m³. |
Example of Air Pressure Speed Calculator
Imagine a scenario in an automotive testing facility where the air enters a wind tunnel at a total pressure of 101325 Pa and a static pressure of 100000 Pa. Assuming the air density is approximately 1.225 kg/m³:
- Velocity (V) = sqrt(2 * (101325 - 100000) / 1.225)
- Velocity (V) ≈ 24.08 m/s
This calculation shows the air speed in the wind tunnel, providing essential data for analyzing vehicle aerodynamics and making adjustments to improve performance.
Most Common FAQs
Differences in air pressure create a driving force that accelerates air from high to low pressure areas, influencing speed and flow characteristics.
Air density affects the energy required to move the air; denser air means more mass is moving, which can require more energy and affect the speed achieved under the same pressure difference.
This calculator is used in designing HVAC systems, optimizing car aerodynamics, evaluating environmental air flows, and more, where understanding air movement is crucial for system efficiency and safety.