The Acceleration to Force Calculator is a tool designed to help users determine the force exerted on an object when its mass and acceleration are known. This calculator is essential for students, engineers, physicists, and anyone interested in understanding the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
Formula of Acceleration to Force Calculator
To calculate force from acceleration, use Newton's second law of motion. The formula is:
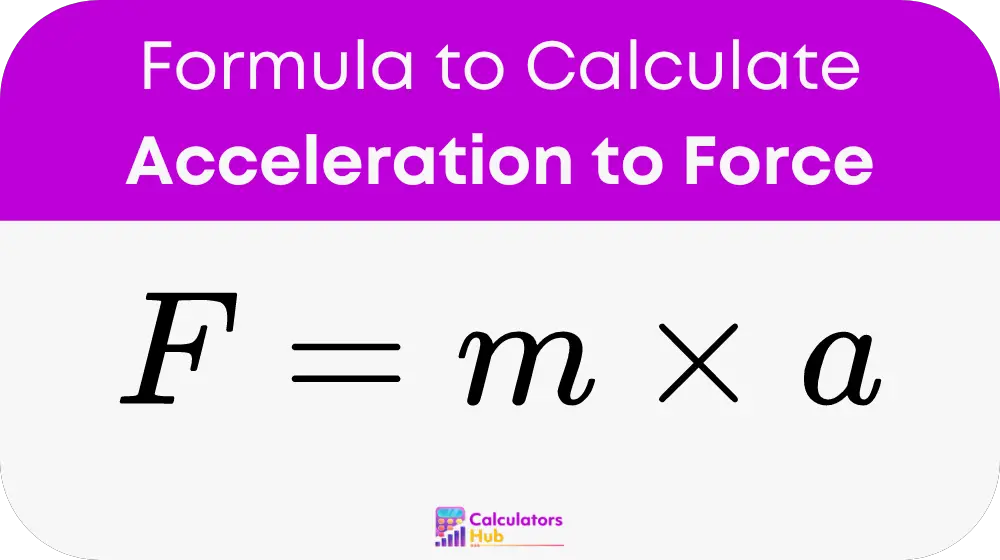
Where:
- F is the force in newtons (N)
- m is the mass in kilograms (kg)
- a is the acceleration in meters per second squared (m/s²)
Steps to Calculate Force from Acceleration:
- Determine the mass (m) of the object in kilograms.
- Measure the acceleration (a) of the object in meters per second squared.
- Multiply the mass by the acceleration to get the force (F).
Pre-calculated Table for Common Searches
To make it easier, here is a table with pre-calculated values for common masses and accelerations:
| Mass (kg) | Acceleration (m/s²) | Force (N) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 4 |
| 5 | 9.8 | 49 |
| 10 | 9.8 | 98 |
| 50 | 9.8 | 490 |
This table can be helpful for quick reference without having to perform the calculations each time.
Example of Acceleration to Force Calculator
Let's go through an example to see how the calculation works:
Suppose you have an object with a mass of 3 kg, and it is accelerating at 4 m/s². To find the force:
- Mass (m) = 3 kg
- Acceleration (a) = 4 m/s²
- Force (F) = m * a = 3 kg * 4 m/s² = 12 N
So, the force exerted on the object is 12 newtons.
Most Common FAQs
The unit of force in the SI system is the newton (N).
To measure mass, use a scale or balance. For acceleration, use an accelerometer or calculate it from the change in velocity over time.
This calculator assumes linear acceleration. For non-linear acceleration, more advanced methods and tools would be needed to calculate force accurately.