The Compressor Discharge Pressure Calculator is a tool used to determine the pressure of a gas after it has been compressed. This is essential for optimizing the performance of compressors in various applications, such as industrial processes, refrigeration, and pneumatic systems. By accurately calculating the discharge pressure, engineers can ensure that the compressor operates within safe and efficient parameters.
Why Is It Important?
Discharge pressure is a critical factor in compressor operation. If the pressure is too high, it can lead to system inefficiencies, overheating, and potential damage. Conversely, if it is too low, the system may not function effectively. This calculator simplifies the process of determining discharge pressure, helping users make informed decisions.
Formula of Compressor Discharge Pressure Calculator
The Compressor Discharge Pressure Calculator uses the following formula:
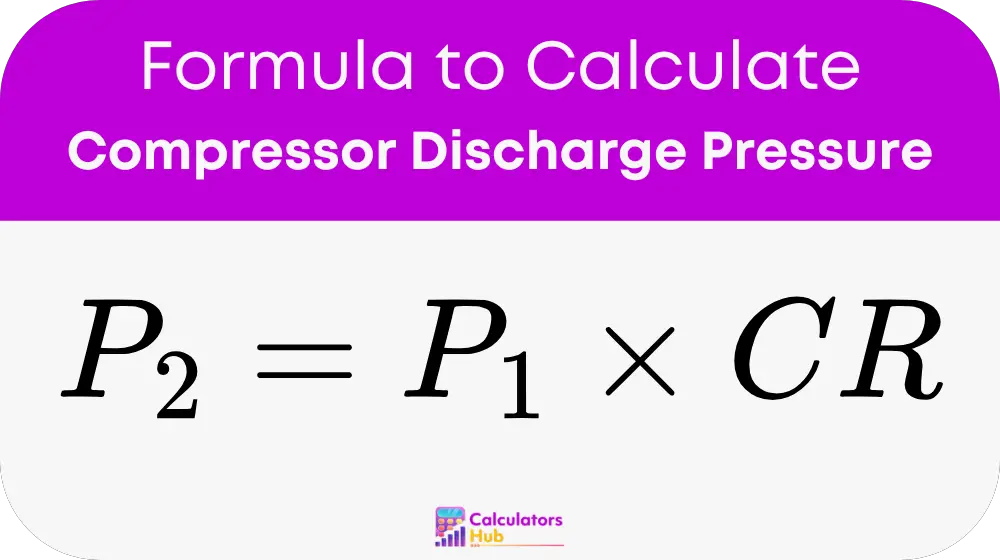
Variables
- P₂: Discharge pressure (absolute, in the same units as P₁).
- P₁: Inlet pressure (absolute, in bar, psi, or any other pressure unit).
- CR: Compression ratio (volume before compression / volume after compression).
Steps to Calculate
- Determine the Inlet Pressure (P₁):
- If the inlet pressure is given as gauge pressure, convert it to absolute pressure:
P₁ (absolute) = P₁ (gauge) + atmospheric pressure. - Atmospheric pressure is typically 14.7 psi or 1.013 bar at sea level.
- If the inlet pressure is given as gauge pressure, convert it to absolute pressure:
- Determine the Compression Ratio (CR):
- If the volumes are given:
CR = V₁ / V₂, where:- V₁ = initial (uncompressed) volume.
- V₂ = final (compressed) volume.
- If the volumes are given:
- Substitute Values into the Formula:
- Multiply the absolute inlet pressure by the compression ratio to calculate the discharge pressure:
P₂ = P₁ × CR.
- Multiply the absolute inlet pressure by the compression ratio to calculate the discharge pressure:
Pre-calculated Table for Common Scenarios
Below is a table showing discharge pressures for common inlet pressures and compression ratios:
| Inlet Pressure (P₁, psi) | Compression Ratio (CR) | Discharge Pressure (P₂, psi) |
|---|---|---|
| 14.7 | 2 | 29.4 |
| 14.7 | 3 | 44.1 |
| 20.0 | 2 | 40.0 |
| 20.0 | 4 | 80.0 |
This table provides quick reference values for typical compression scenarios.
Example of Compressor Discharge Pressure Calculator
Scenario
A compressor takes in air at an inlet pressure of 14.7 psi (absolute) and compresses it with a compression ratio of 3:1. Calculate the discharge pressure.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Determine the Inlet Pressure (P₁):
P₁ = 14.7 psi (absolute). - Determine the Compression Ratio (CR):
CR = 3. - Apply the Formula:
P₂ = P₁ × CR
P₂ = 14.7 × 3
P₂ = 44.1 psi.
Thus, the discharge pressure is 44.1 psi.
Most Common FAQs
The calculator determines the pressure of gas after compression, ensuring the system operates efficiently and safely.
Yes, the formula is applicable for any compressible gas. However, you may need to account for specific gas properties in more advanced calculations.
Absolute pressure accounts for atmospheric pressure, providing a true measure of the total pressure exerted by the gas, which is essential for accurate calculations.