The Colebrook Formula Calculator is a specialized tool used to determine the Darcy-Weisbach friction factor (f), which is essential for calculating head loss in fluid flow through pipes. The Colebrook equation is implicit and applies to turbulent flow in rough or smooth pipes. This calculator automates the iterative process required to solve the equation, saving engineers and fluid dynamics professionals significant time and effort. It belongs to the category of hydraulic and fluid mechanics tools, providing precise solutions for designing and analyzing pipe systems.
Formula of Colebrook Formula Calculator
The Colebrook equation is given as:
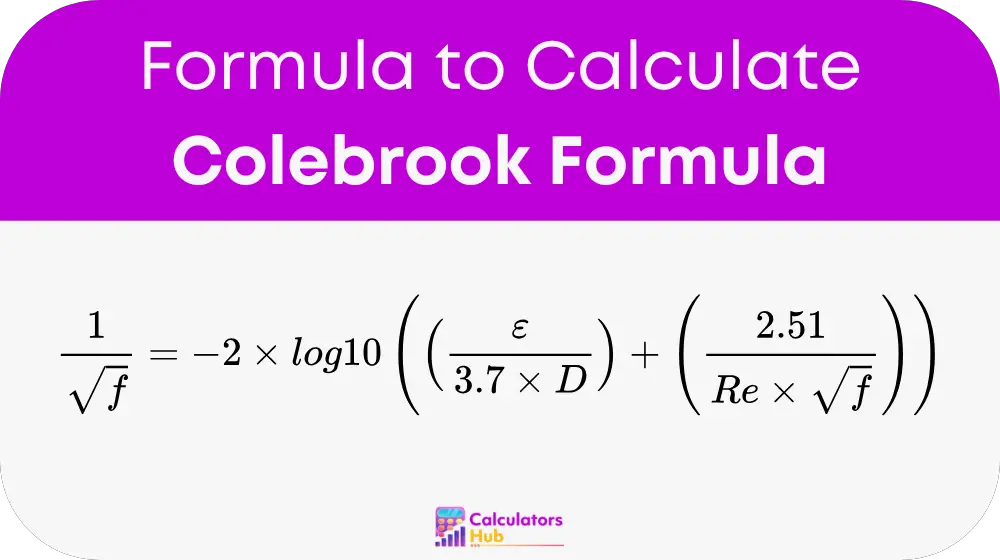
Where:
- f is the Darcy-Weisbach friction factor.
- ε is the absolute roughness of the pipe (in meters).
- D is the pipe diameter (in meters).
- Re is the Reynolds number (dimensionless).
Detailed Formulas for Variables
Reynolds Number (Re):
The Reynolds number is calculated as:
Re = (ρ * v * D) / μ
Where:
- ρ is the fluid density (in kilograms per cubic meter).
- v is the flow velocity (in meters per second).
- D is the pipe diameter (in meters).
- μ is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid (in pascal-seconds).
Absolute Roughness (ε):
The absolute roughness is a material property representing the surface roughness of the pipe. Common values include:
- Steel: ~0.000045 meters.
- PVC: ~0.0000015 meters.
By substituting these variables into the Colebrook equation, users can compute the friction factor and use it to calculate head loss or pressure drop in the pipe.
Pre-Calculated Table for Common Pipe Materials and Conditions
Below is a reference table showcasing typical absolute roughness values and corresponding Reynolds numbers:
| Pipe Material | Absolute Roughness (ε) | Reynolds Number (Re) | Friction Factor (f) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | 0.000045 | 10⁵ | 0.018 |
| Cast Iron | 0.00026 | 10⁶ | 0.015 |
| PVC | 0.0000015 | 10⁵ | 0.012 |
| Concrete | 0.0003 | 10⁶ | 0.02 |
This table simplifies the initial estimation of friction factors for common scenarios.
Example of Colebrook Equation Calculator
Let’s calculate the Darcy-Weisbach friction factor for a steel pipe with the following parameters:
- Pipe diameter (D): 0.1 meters.
- Flow velocity (v): 2 m/s.
- Fluid density (ρ): 1000 kg/m³.
- Dynamic viscosity (μ): 0.001 Pa·s.
- Absolute roughness (ε): 0.000045 meters.
Step 1: Calculate the Reynolds Number (Re)
Re = (ρ * v * D) / μ
Re = (1000 * 2 * 0.1) / 0.001 = 200,000.
Step 2: Substitute into the Colebrook Equation
The equation becomes:
1 / sqrt(f) = -2 * log10((0.000045 / (3.7 * 0.1)) + (2.51 / (200,000 * sqrt(f)))).
Step 3: Iterative Solution
Using numerical methods or a calculator:
f ≈ 0.018.
Thus, the Darcy-Weisbach friction factor is approximately 0.018.
Most Common FAQs
The Colebrook equation is essential for calculating the friction factor, which influences the pressure drop and energy requirements in pipe systems. It is widely used in engineering for system design and analysis.
No, the Colebrook equation is implicit and requires iterative or approximate methods to solve. Many calculators and software tools automate this process.
Absolute roughness (ε) is a material property, while relative roughness is the ratio of absolute roughness to pipe diameter (ε/D). The relative roughness is used directly in the Colebrook equation.