The Chvorinov’s Rule Calculator is a tool designed to estimate the solidification time of metal castings. Solidification time is a critical factor in metal casting, affecting the final quality, surface finish, and mechanical properties of the cast product. By using the formula derived from Chvorinov’s Rule, the calculator helps manufacturers and engineers determine the appropriate cooling time required to produce castings with minimal defects. This rule is particularly useful in industries like foundry work and casting manufacturing, where controlling the solidification process is essential for achieving high-quality products.
The formula provided by Chvorinov’s Rule takes into account the volume of the casting, the surface area exposed to the environment, and the mold characteristics. The calculator helps users predict how long it will take for molten metal to cool and solidify completely in the mold. The result can guide decisions about mold design, pouring temperature, and casting material to optimize the manufacturing process.
Formula of Chvorinov’s Rule Calculator
The solidification time for metal casting can be estimated using Chvorinov’s Rule with the following formula:
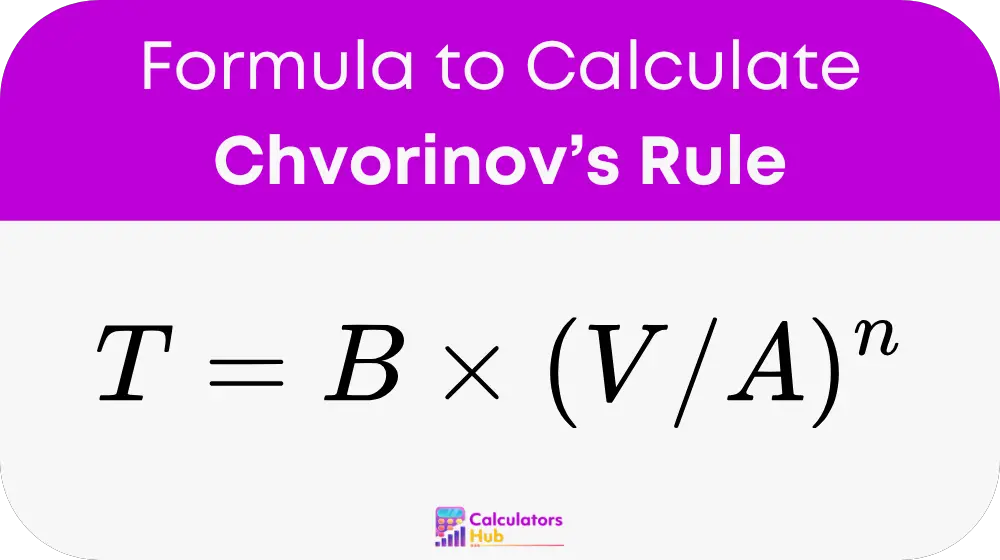
Where:
- T is the solidification time in seconds,
- B is a mold constant, which varies depending on the material of the mold and the pouring temperature,
- V is the volume of the casting in cubic centimeters,
- A is the surface area of the casting in square centimeters,
- n is Chvorinov’s constant, which typically ranges from 1.5 to 2.0 depending on the properties of the casting material and the mold material.
This formula helps in predicting the cooling and solidification rates by considering both the geometry of the casting and the heat transfer properties of the mold material.
Factors Affecting Solidification Time
Several factors influence the solidification time of metal castings:
- Material Properties: The type of material used for the casting, such as aluminum, steel, or bronze, can significantly affect the solidification rate. Materials with high thermal conductivity tend to cool faster.
- Mold Material: The mold’s composition, whether it is made of sand, metal, or other materials, impacts the heat transfer rate. Molds with higher heat conductivity will allow faster solidification.
- Pouring Temperature: The temperature at which the molten metal is poured into the mold also influences the solidification time. Higher pouring temperatures lead to longer cooling times.
- Casting Geometry: Complex or thicker parts with more volume tend to take longer to cool compared to simpler, smaller castings. The surface area-to-volume ratio (A/V) plays a crucial role in this.
A Table for Common Terms and Conversions
To help you better understand and use the Chvorinov’s Rule Calculator, here’s a table with general casting-related terms and conversion factors:
| Term | Description | Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Volume (V) | The total volume of the casting in cubic centimeters (cm³). | 1 cm³ = 0.001 L |
| Surface Area (A) | The total surface area of the casting in square centimeters (cm²). | 1 cm² = 0.0001 m² |
| Mold Constant (B) | A factor specific to the mold material and pouring temperature. | No standard conversion, depends on material. |
| Solidification Time (T) | The time required for the molten metal to solidify in seconds. | Directly calculated from the formula. |
Example of Chvorinov’s Rule Calculator
Let’s go through an example to calculate the solidification time using Chvorinov’s Rule.
Suppose we have a metal casting with the following parameters:
- Volume (V) = 500 cm³
- Surface Area (A) = 200 cm²
- Mold Constant (B) = 10
- Chvorinov’s Constant (n) = 1.8
Now, plug these values into the formula:
T = 10 * (500 / 200)^1.8
T ≈ 10 * 6.77 ≈ 67.7 seconds
The estimated solidification time is approximately 67.7 seconds.
Most Common FAQs
The mold constant (B) is a factor specific to the material of the mold and the pouring temperature. It influences how quickly heat is transfer from the casting to the mold. The higher the B value, the slower the solidification process will be. The exact value of B is determine experimentally or base on industry standards for specific materials.
Chvorinov’s Rule is widely use in foundry work for various metals, but it is more accurate for metals with similar thermal properties. It may need adjustments or additional factors for specific alloys or casting conditions, especially when using non-standard mold materials.
By using the Chvorinov’s Rule Calculator, foundries can predict solidification time more accurately. This allows for better control of the casting process, minimizing defects such as cold shuts, shrinkage, or cracks caused by uneven solidification.