The Chronotropic Response Index (CRI) Calculator is a tool used to assess how well your heart responds to exercise, specifically the ability of the heart rate to increase during physical activity. This response is crucial for evaluating cardiovascular health and fitness. By calculating the CRI, healthcare professionals and fitness experts can determine if a person’s heart is responding normally to exertion or if there may be issues, such as chronotropic incompetence, where the heart fails to achieve an adequate increase in heart rate during exercise. The CRI provides insights into heart function and can help identify potential health concerns. This tool is commonly used in clinical and fitness settings to assess cardiovascular function.
Formula of Chronotropic Response Index Calculator
The formula for calculating the Chronotropic Response Index (CRI) is:
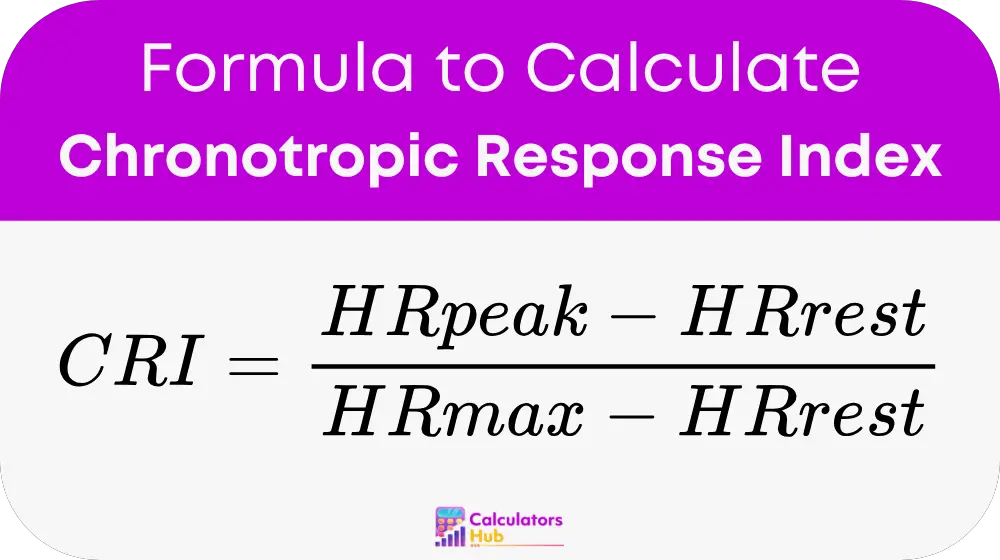
Where:
- HRpeak: Peak heart rate achieved during exercise
- HRrest: Resting heart rate
- HRmax: Maximum predicted heart rate, commonly calculated as 220 – age
Interpretation of CRI:
- CRI > 0.8: This indicates a normal chronotropic response, meaning the heart is able to increase its rate sufficiently during exercise.
- CRI < 0.8: This suggests an impaired chronotropic response, which may indicate chronotropic incompetence, a condition where the heart does not respond adequately to exercise.
Pre-Calculated Values Table
For those who want a quick reference or do not want to perform the calculation manually, here is a table of general values for CRI interpretation. These values can help you understand what to expect based on different age groups and resting heart rates.
| Age (years) | Resting Heart Rate (HRrest) | HRpeak (After Exercise) | Maximum Predicted HR (HRmax) | CRI Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 60 | 185 | 195 | Normal (0.81) |
| 40 | 70 | 160 | 180 | Normal (0.67) |
| 55 | 75 | 145 | 165 | Impaired (0.53) |
| 60 | 80 | 140 | 160 | Impaired (0.44) |
This table provides a quick guide to interpreting CRI values for various age groups and can help identify potential issues with chronotropic response.
Example of Chronotropic Response Index Calculator
Let’s calculate the CRI for a 35-year-old individual with the following information:
- Resting heart rate (HRrest) = 65 bpm
- Peak heart rate during exercise (HRpeak) = 175 bpm
- Maximum predicted heart rate (HRmax) = 220 – 35 = 185 bpm
Using the formula:
CRI = (175 – 65) / (185 – 65)
CRI = 110 / 120 = 0.92
This result indicates a normal chronotropic response, as the CRI is greater than 0.8.
Most Common FAQs
Chronotropic incompetence refers to a condition where the heart fails to increase its rate adequately during exercise. This could be a sign of underlying cardiovascular issues, such as heart disease or autonomic dysfunction, and may require further medical evaluation.
Improving cardiovascular fitness through regular aerobic exercise, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, can help improve your heart’s ability to increase its rate during exercise. Consult with a healthcare professional or fitness expert to create a safe and effective exercise plan.
While CRI is a useful tool, it is just one aspect of assessing cardiovascular health. Other methods, such as resting heart rate, blood pressure, and stress tests, can also provide valuable insights into heart function and overall fitness.