The BTU to Volume Calculator is a tool that helps users convert energy measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs) into the corresponding volume of fuel required to produce that energy. Whether you are dealing with natural gas, propane, or other fuel types, this calculator allows users to estimate the amount of fuel needed to meet energy requirements. It’s particularly useful in heating, HVAC, and energy management industries where understanding fuel consumption is critical for cost control and efficiency.
For anyone needing to plan fuel purchases, track consumption, or optimize energy usage, this calculator simplifies the process by converting BTUs into a measurable volume of fuel.
Why You Need a BTU to Volume Calculator
- Energy Efficiency: It helps optimize fuel usage by accurately converting energy needs into fuel volume, allowing for better planning and resource management.
- Cost Management: By understanding fuel consumption in volume, you can estimate fuel costs more accurately and budget effectively.
- System Performance: HVAC professionals and engineers can use the calculator to ensure that systems are operating efficiently and within the designed energy parameters.
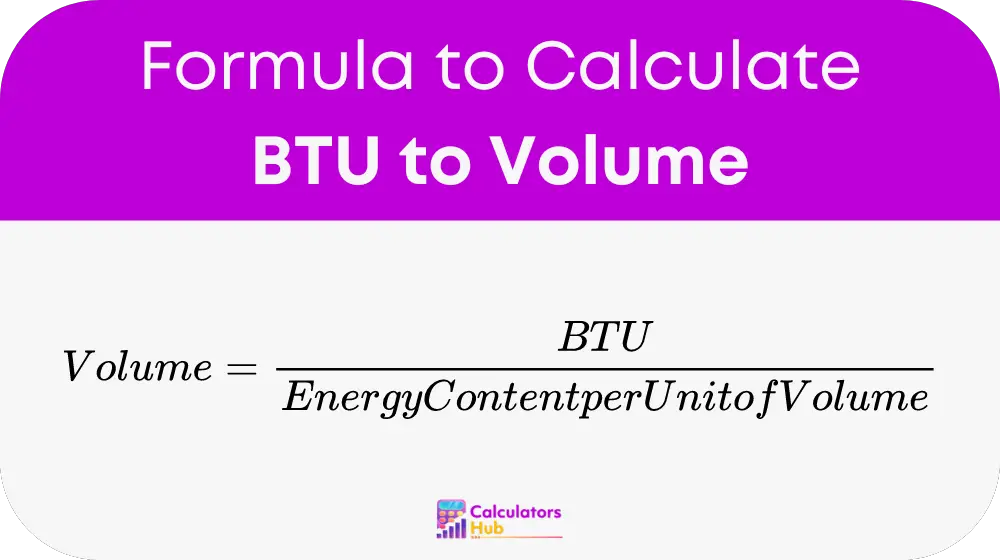
Formula
The formula to convert BTUs into volume is as follows:
Variables:
- Volume: The amount of fuel required, typically measured in cubic feet, gallons, or liters.
- BTU: The energy needed, measured in British Thermal Units (BTU).
- Energy Content per Unit of Volume: The amount of energy contained in a specific volume of fuel. For example:
- Natural Gas: ~1,037 BTU per cubic foot
- Propane: ~91,500 BTU per gallon
- Fuel Oil: ~138,500 BTU per gallon
This formula allows you to determine how much fuel is necessary to produce a given amount of energy, making it essential for energy planning and consumption tracking.
Pre-calculated BTU to Volume Conversions
Here’s a table showing common BTU values and the corresponding volumes of different fuels required to meet those energy demands. This table can be useful for quick reference and for estimating fuel needs.
| BTU (Energy Input) | Natural Gas (Cubic Feet) | Propane (Gallons) | Fuel Oil (Gallons) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 BTU | 9.64 cubic feet | 0.11 gallons | 0.07 gallons |
| 50,000 BTU | 48.23 cubic feet | 0.55 gallons | 0.36 gallons |
| 100,000 BTU | 96.47 cubic feet | 1.09 gallons | 0.72 gallons |
| 500,000 BTU | 482.35 cubic feet | 5.46 gallons | 3.61 gallons |
| 1,000,000 BTU | 964.70 cubic feet | 10.92 gallons | 7.22 gallons |
This table provides approximate values to help users understand the fuel requirements for different energy needs.
Example
Let’s work through an example to demonstrate how the BTU to Volume Calculator works:
Scenario: You need to determine how much propane is required to generate 200,000 BTUs of energy for heating purposes.
- Step 1: Identify the known variables:
- BTU = 200,000
- Energy Content of Propane = 91,500 BTU per gallon
- Step 2: Use the formula:Volume = BTU / Energy Content per Unit of Volume
- Step 3: Apply the values:Volume = 200,000 / 91,500 Volume ≈ 2.19 gallons
The result shows that approximately 2.19 gallons of propane are needed to produce 200,000 BTUs of energy.
Most Common FAQs
Converting BTUs to fuel volume is essential for understanding how much fuel you need to meet your energy demands. This is particularly important for budgeting, fuel purchasing, and ensuring that HVAC systems, boilers, or heating units are supplied with the correct amount of fuel for efficient operation.
Yes, the BTU to Volume Calculator can be use for different fuel types, such as natural gas, propane, fuel oil, and more. You simply need to know the energy content per unit of volume for the fuel type you are working with, which can be easily obtained from fuel suppliers or industry standards.
The accuracy of the BTU to Volume Calculator depends on the precision of the energy content values for the specific fuel. Energy content values can vary slightly based on factors such as fuel quality or environmental conditions. However, for most practical purposes, the calculator provides highly accurate estimates that are sufficient for planning and budgeting.