The Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) Calculator is a pivotal tool in the field of medical imaging, specifically in the analysis of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans. This calculator quantifies the diffusion of water molecules within biological tissues, which is crucial for diagnosing conditions such as brain ischemia, tumors, and other pathologies. By assessing how water molecules spread in tissue environments, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into cellular integrity and tissue viability.
Formula for Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Calculator
The calculation of ADC is fundamental in understanding tissue characteristics under various pathological conditions. The formula used is:
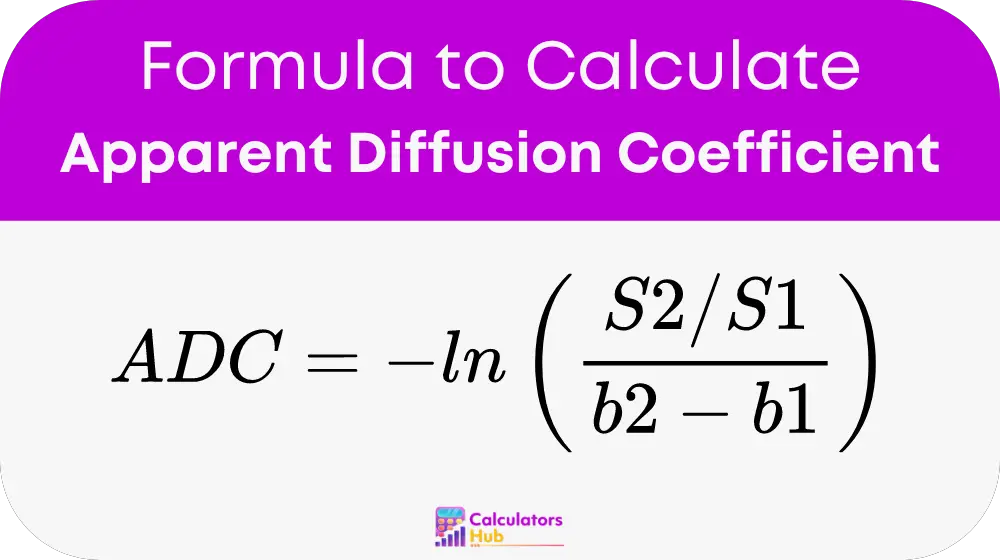
Components of the Formula:
- S1 and S2: Signal intensities at two different diffusion weightings.
- b1 and b2: The diffusion weighting factors corresponding to S1 and S2.
- ln: Natural logarithm, reflecting the logarithmic decay of signal intensity due to diffusion.
This formula provides a measure of the diffusion coefficient, which helps in distinguishing between different types of tissue based on how freely water molecules are moving in the area.
Calculation Process:
- Collect Signal Intensities: Obtain the MRI signal intensities with two different diffusion weighting factors.
- Apply the Formula: Input these values into the formula to compute the ADC.
- Analyze the Results: Use the ADC values to aid in clinical diagnosis and treatment planning.
Practical Application: Reference Table
Here is a simple table illustrating typical ADC values across different brain tissues, which helps in diagnosing various conditions:
| Tissue Type | ADC Value (x10^-3 mm^2/s) | Typical Clinical Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Brain | 0.7 - 0.9 | Normal range for healthy tissue |
| Ischemic Stroke | 0.4 - 0.5 | Reduced diffusion due to stroke |
| High-grade Tumors | 1.0 - 1.5 | Increased diffusion in malignant cells |
This table enables clinicians to quickly reference expected ADC values for different conditions, enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Example of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Calculator
Consider an MRI scan where:
- S1 (signal intensity with b-value of 0 s/mm²): 1000
- S2 (signal intensity with b-value of 1000 s/mm²): 400
- b1: 0 s/mm²
- b2: 1000 s/mm²
Using the formula:
- ADC = -ln(400 / 1000) / (1000 - 0) = -ln(0.4) / 1000 ≈ 0.916 / 1000 = 0.000916 mm²/s
This ADC value can be interpreted in the context of the tissue type and the clinical scenario to assist in diagnosis.
Most Common FAQs
A low ADC value typically indicates restricted diffusion, often seen in acute stroke, where water movement is hindered by swollen cells.
ADC values can differentiate between benign and malignant lesions, as malignant tissues tend to have higher ADC values due to increased cellularity and necrosis.
In some cases, changes in ADC values over time can provide insights into the effectiveness of treatments, particularly in monitoring tumor response in oncology.