The A-A Gradient measures the difference between the oxygen concentration in the alveoli (PAO2) and the arterial blood (PaO2). This measurement is crucial for evaluating the lungs’ ability to transfer oxygen from the air into the blood. It is particularly vital in diagnosing and managing patients with suspected respiratory impairments.
Clinical Relevance
In clinical practice, an abnormal A-A Gradient can be indicative of serious health issues, such as a pulmonary embolism or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). By providing a clear metric of lung efficiency, the A-A Gradient Calculator assists healthcare providers in making informed decisions quickly.
Formula of A-A Gradient Calculator
Equation Presentation
To calculate the A-A Gradient, use the formula:
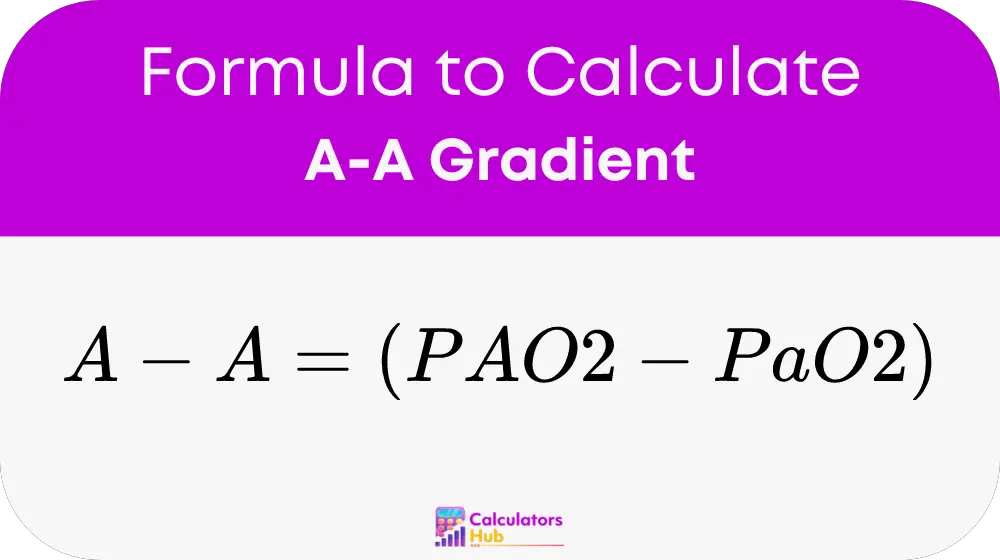
Component Definitions
PAO2 Calculation
PAO2, or the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli, is calculated using the alveolar gas equation:
PAO2=(FiO2×(PB−PH2O))−(PaCO2/R)
Where FiO2 is the fraction of inspired oxygen, PB is the barometric pressure, PH2O is the water vapor pressure, PaCO2 is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood, and R is the respiratory quotient.
PaO2 Estimation
PaO2, or the partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood, is estimated by:
PaO2=(SaO2×(Pbar−47))+(0.0031×PaCO2)
Where SaO2 is the oxygen saturation of arterial blood.
Table of Common Values
| FiO2 (%) | FiO2 (Decimal) | Estimated PAO2 (mmHg) | SaO2 (%) | Estimated PaO2 (mmHg) | A-A Gradient (mmHg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | 0.21 | 100 | 98 | 104 | -4 |
| 24 | 0.24 | 122 | 98 | 104 | 18 |
| 28 | 0.28 | 143 | 98 | 104 | 39 |
| 32 | 0.32 | 165 | 98 | 104 | 61 |
| 40 | 0.40 | 200 | 98 | 104 | 96 |
| 60 | 0.60 | 300 | 98 | 104 | 196 |
| 100 | 1.00 | 713 | 98 | 104 | 609 |
Example of A-A Gradient Calculator
Consider a patient at sea level with the following parameters: FiO2 of 0.21, PB of 760 mmHg, PH2O of 47 mmHg, PaCO2 of 40 mmHg, R of 0.8, SaO2 of 97%, and PaCO2 again at 40 mmHg.
Using the formulas:
PAO2=(0.21×(760−47))−(40/0.8)≈100 mmHg
PaO2=(0.97×(760−47))+(0.0031×40)≈104 mmHg
A-a gradient=100−104=−4 mmHg
A negative A-A Gradient suggests a potential measurement error or extraordinary physiological circumstances, warranting further investigation.
Most Common FAQs
A high A-A Gradient typically indicates a potential barrier to oxygen transfer from the alveoli to the bloodstream, which could be due to pulmonary embolism, fibrosis, or early signs of COPD.
At higher altitudes, barometric pressures decrease, necessitating recalculations of the A-A Gradient to adjust for these changes accurately.
Yes, but the FiO2 variable must be correctly adjusted to reflect the increased inhaled oxygen concentration, which will alter the gradient calculation.