The Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) Calculator is a vital tool used in the banking and finance industry to assess a bank's financial stability and risk management capabilities. The CAR is a measure that indicates a bank's available capital in relation to its risk-weighted assets. By using this calculator, banks can determine whether they hold sufficient capital to cover potential losses, thereby ensuring the protection of depositors and maintaining the overall stability of the financial system. This calculator is essential for regulatory compliance and helps financial institutions make informed decisions regarding capital allocation and risk management.
Formula of Capital Adequacy Ratio Calculator
The formula to calculate the Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is:
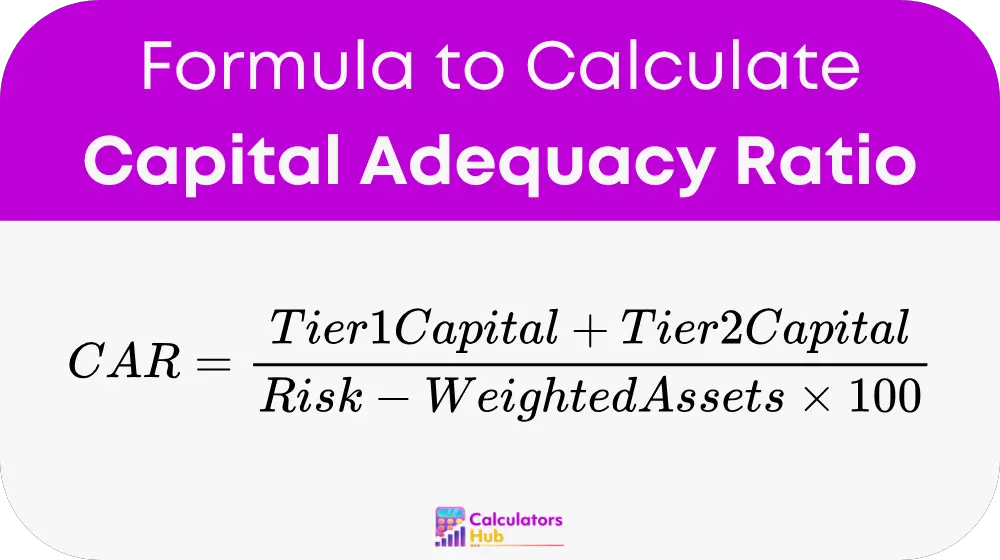
where:
- CAR is the capital adequacy ratio expressed as a percentage.
- Tier 1 Capital includes core capital, such as common equity and disclosed reserves.
- Tier 2 Capital includes supplementary capital, like subordinated debt and revaluation reserves.
- Risk-Weighted Assets are the bank's assets weighted according to their associated credit, market, and operational risks.
General Terms Table
The following table provides common terms related to capital adequacy and banking metrics, serving as a helpful reference for users without needing to perform calculations each time.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) | A measure of a bank's capital in relation to its risk-weighted assets, expressed as a percentage. |
| Tier 1 Capital | The core capital of a bank, consisting mainly of common equity and disclosed reserves. |
| Tier 2 Capital | Supplementary capital that includes subordinated debt and revaluation reserves. |
| Risk-Weighted Assets | A bank's assets adjusted for their risk level, reflecting the potential for financial loss. |
| Common Equity | A bank's ownership interest held by common shareholders, representing the most stable form of capital. |
| Subordinated Debt | A form of debt that ranks lower in priority for repayment compared to other debts. |
Example of Capital Adequacy Ratio Calculator
To illustrate the use of the Capital Adequacy Ratio Calculator, consider a hypothetical bank with the following data:
- Tier 1 Capital: $500 million
- Tier 2 Capital: $200 million
- Risk-Weighted Assets: $3 billion
Using the formula:
CAR = ($500 million + $200 million) / $3 billion * 100
CAR = $700 million / $3 billion * 100 = 23.33%
In this example, the capital adequacy ratio of the bank is 23.33%. This indicates that the bank has a robust capital position, well above the minimum regulatory requirement, which is typically around 8% for most banks.
Most Common FAQs
The minimum capital adequacy ratio generally required by regulators is 8%. However, many banks aim for a higher ratio to ensure they have enough capital to absorb potential losses.
The capital adequacy ratio is crucial because it helps ensure that banks can withstand financial shocks and continue operations even in adverse conditions. It protects depositors and promotes stability in the financial system.
A bank can improve its capital adequacy ratio by increasing its Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital through retained earnings, issuing new equity, or reducing risk-weighted assets by improving asset quality or reducing leverage.