The Energy Transfer Efficiency Calculator is a practical tool used to determine how efficiently energy is converted or transferred within a system. It calculates the ratio of useful energy output to the total energy input, expressed as a percentage. This concept is widely apply in power plants, mechanical systems, electronics, industrial processes, and even biological systems. The calculator belongs to the Energy Conversion and System Performance Calculator category.
By using this calculator, engineers, energy analysts, students, and sustainability experts can assess how much energy is being lost during transfer and identify opportunities for improvement.
Formula of Energy Transfer Efficiency Calculator
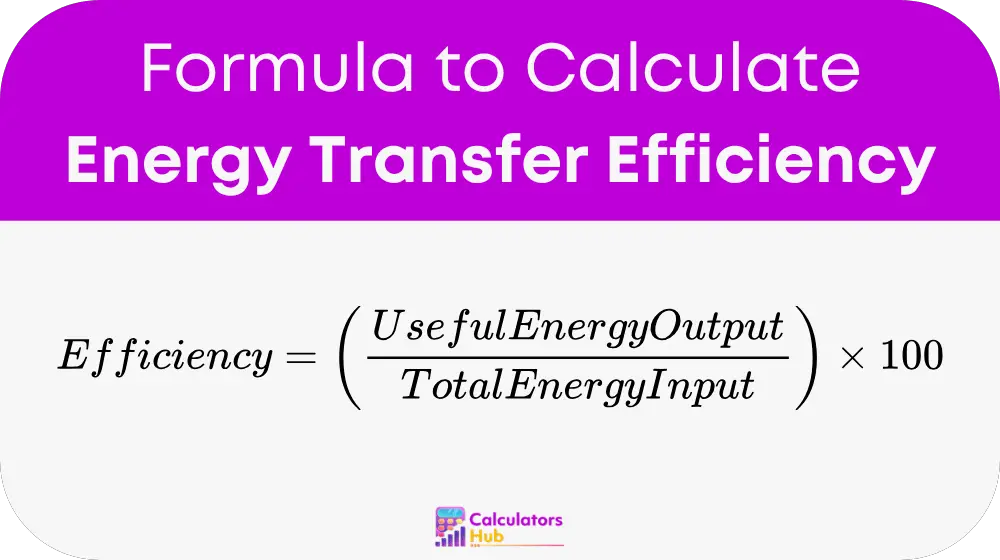
Detailed Breakdown:
- Useful Energy Output
The amount of energy that is effectively use to perform the desire task. This can be in the form of mechanical work, heat, motion, or electricity (measured in joules, kilowatt-hours, etc.) - Total Energy Input
The total energy supplied to the system or process. It must be measure in the same unit as the output for accuracy.
This formula provides a clear indication of how well a system is converting input energy into productive work. The closer the value is to 100%, the more efficient the system is.
Quick Reference Table
This table lists common real-world systems and their approximate energy transfer efficiency values. These benchmarks can help users quickly compare and evaluate system performance.
| System/Process | Total Energy Input | Useful Energy Output | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modern Electric Motor | 1000 J | 950 J | 95 |
| Incandescent Light Bulb | 1000 J | 100 J | 10 |
| Internal Combustion Engine (Car) | 1000 J | 300 J | 30 |
| Solar Panel (Standard Efficiency) | 1000 J | 180 J | 18 |
| LED Light Bulb | 1000 J | 250 J | 25 |
These values highlight how efficiency can vary widely depending on technology and design.
Example of Energy Transfer Efficiency Calculator
Let’s say a heating system receives 20,000 joules of energy and delivers 15,000 joules as usable heat.
Step 1:
Use the formula:
Efficiency = (15,000 / 20,000) × 100 = 0.75 × 100 = 75%
This means the heating system has an energy transfer efficiency of 75%, indicating that 25% of the energy is lost, likely as unused heat, radiation, or friction.
Most Common FAQs
That depends on the system. Electric motors can reach 90–95%, while combustion engines are often below 40%. In general, the higher the percentage, the more efficient the system.
Yes, as long as the input and output use the same unit (e.g., both in joules, kWh, etc.), the formula will work correctly.
Efficiency determines how much energy is wasted. Improving efficiency lowers energy costs, reduces emissions, and enhances overall system performance.