A CT Ratio to Current Calculator helps engineers, electricians, and power system operators determine the secondary current in a current transformer (CT) based on the primary current and CT ratio. Current transformers are used in power distribution, metering, and protection systems to step down high electrical currents to safer levels for measurement.
This calculator is essential for ensuring accurate current measurements, verifying metering equipment, and designing electrical protection systems. By using the CT ratio, professionals can determine the actual current flowing through the secondary side of the transformer for monitoring and protection purposes.
Formula of CT Ratio to Current Calculator
The secondary current (Is) in a current transformer is calculated using the following formula:
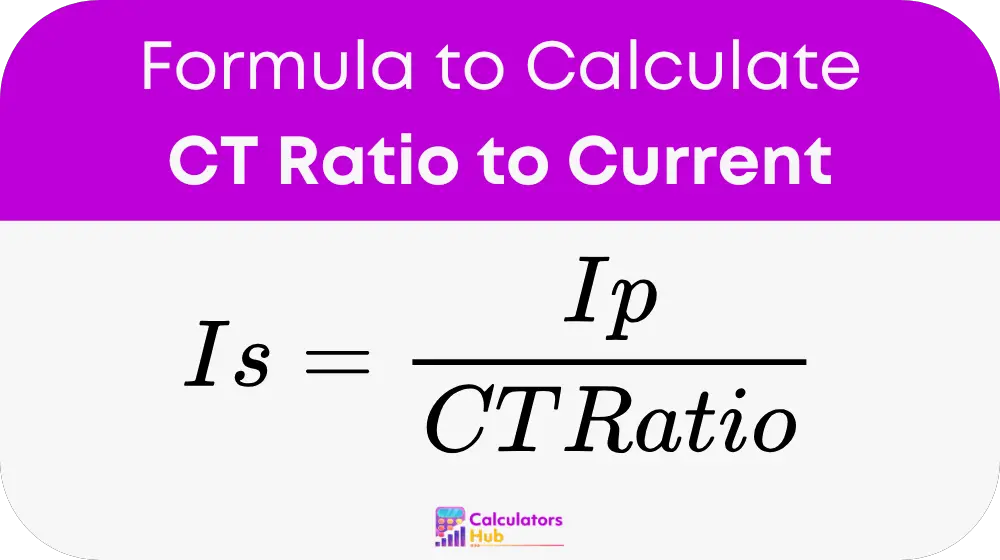
Where:
- Is = Secondary Current (the current measured on the secondary side of the transformer).
- Ip = Primary Current (the current flowing through the primary side of the transformer).
- CT Ratio = The ratio of the primary current to the secondary current (for example, a 100:5 CT ratio means that for every 100A in the primary circuit, 5A is present in the secondary circuit).
This formula ensures precise scaling of high electrical currents into manageable levels for metering and protection devices.
Pre-Calculated CT Ratio to Current Table
For quick reference, here is a table of secondary currents for common CT ratios and primary current values:
| Primary Current (A) | CT Ratio | Secondary Current (A) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 200:5 | 25 |
| 800 | 160:5 | 25 |
| 600 | 120:5 | 25 |
| 400 | 80:5 | 25 |
| 200 | 40:5 | 25 |
| 100 | 20:5 | 25 |
This table helps electrical engineers and technicians quickly determine secondary current values without manual calculations.
Example of CT Ratio to Current Calculator
Let’s calculate the secondary current for a system where:
- Primary current (Ip) = 800 A
- CT Ratio = 160:5
Applying the formula:
Is = 800 / (160/5)
Is = 800 / 32 = 25 A
Thus, the secondary current is 25 A, meaning the metering and protection devices will measure 25 A instead of the actual 800 A primary current.
Most Common FAQs
The CT ratio ensures safe current measurement, allowing electrical meters and protection relays to accurately monitor high-voltage systems without handling dangerous current levels.
The CT ratio should be chosen based on the maximum expected primary current and the required secondary current (usually 5A or 1A for standard metering and relays).
Using an incorrect CT ratio can result in incorrect meter readings, relay malfunctions, and potential system failures, affecting the efficiency and safety of an electrical network.