The Apparent Power Calculator is an essential tool in electrical engineering, designed to compute the total power in an electrical circuit without distinguishing between the energy converted to useful work and the energy lost. Apparent power, expressed in volt-amperes (VA), is crucial for sizing electrical components such as wiring, transformers, and generators, ensuring they handle loads without overheating or other risks.
Formula for Apparent Power Calculator
The calculation of apparent power (S) integrates both real power (P) and reactive power (Q), providing a holistic view of the energy flowing in a circuit:
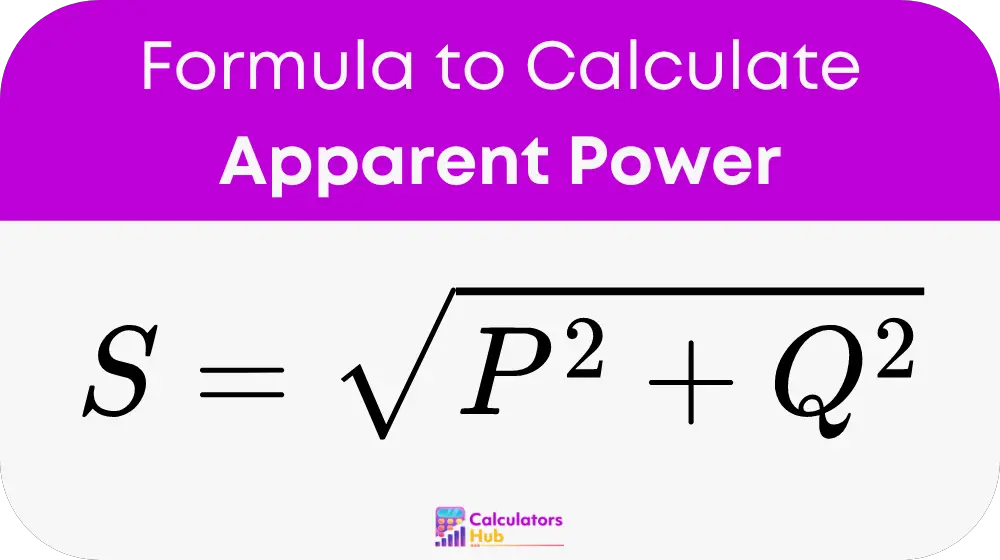
Detailed Breakdown:
- S: Apparent power in volt-amperes (VA).
- P: Real power, which performs actual work, in watts (W).
- Q: Reactive power, which sustains the electromagnetic field, in volt-amperes reactive (VAR).
This formula is vital for understanding how much power a system requires to operate efficiently without actual energy conversion.
Practical Application: Reference Table
For clarity, here’s a table demonstrating different scenarios of real and reactive power and their corresponding apparent power:
| Real Power (W) | Reactive Power (VAR) | Apparent Power (VA) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0 | 100 |
| 50 | 50 | 70.71 |
| 100 | 100 | 141.42 |
| 0 | 50 | 50 |
This table helps illustrate how variations in real and reactive power affect the total apparent power, guiding the design and troubleshooting of electrical systems.
Example of Apparent Power Calculator
Consider a circuit with 300 watts of real power and 400 VAR of reactive power. Using the apparent power formula:
- Real Power (P): 300 W
- Reactive Power (Q): 400 VAR
Plugging into the formula:
- Apparent Power (S) = √(300^2 + 400^2) = √(90000 + 160000) = √250000 = 500 VA
This example clearly demonstrates how to calculate the apparent power, showing the relationship between real, reactive, and apparent power.
Most Common FAQs
Real power accomplishes effective work, reactive power supports magnetic and electric fields, and apparent power is the vector sum of real and reactive power, representing the total power supplied to the circuit.
Apparent power is crucial for designing electrical systems, as it determines the capacity needed for electrical components to operate safely under various loads, preventing system failures.
The phase angle between the current and voltage directly influences the relationship between real, reactive, and apparent power. Larger angles increase reactive power, affecting the apparent power required for system stability.