The Galvanic cell calculator provides a user-friendly interface for calculating the potential of Galvanic cells under various conditions. This tool is essential for anyone dealing with electrochemistry, as it helps predict cell behavior and make accurate adjustments in experiments and industrial applications.
Formula of Galvanic Cell Calculator
At the heart of the calculator is the formula:
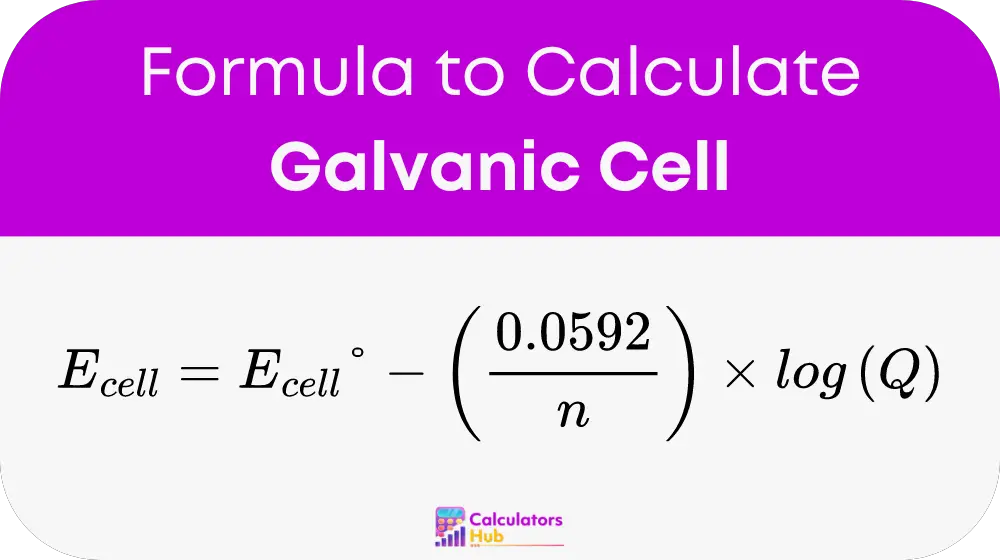
This formula calculates the cell potential under non-standard conditions, incorporating:
- Ecell°: the standard cell potential which provides a baseline measurement of the cell’s capability.
- n: the number of moles of electrons transferred, affecting the potential directly.
- Q: the reaction quotient, indicating the ratio of product and reactant concentrations at any given moment.
Useful Conversion Table
| Term | Definition | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Cell Potential (E°) | The voltage between two half-cells in a standard state | Used as E° in the formula |
| Cell Potential (Ecell) | The voltage under non-standard conditions | Output of the calculator |
| Number of Moles (n) | Moles of electrons transferred in the reaction | Affects the calculation of Ecell |
| Reaction Quotient (Q) | Ratio of product concentrations to reactant concentrations | Input for the formula; varies in each case |
| Log(Q) | Logarithm of the reaction quotient | Part of the formula to adjust Ecell |
| Concentration | Amount of a substance per defined space | Used to calculate Q |
| Stoichiometric Coefficients | Numbers that balance the reaction in a chemical equation | Used to raise concentrations in Q |
Example of Galvanic Cell Calculator
Let’s use the Galvanic cell calculator for a zinc-copper cell where the zinc electrode is the anode and the copper electrode is the cathode. Assume standard conditions with:
- Ecell° (Zn/Cu): +1.10 V (standard potential difference)
- n: 2 (moles of electrons transferred per mole of zinc and copper reaction)
- Q: 1 (reaction quotient under standard conditions)
Input these values into the calculator:
- Ecell° = +1.10 V
- n = 2
- Q = 1
Calculator output:
- Ecell: +1.10 V
Most Common FAQs
The standard cell potential is a critical factor that indicates the maximum potential difference between the electrodes when no current is flowing.
The more moles of electrons involved in the reaction, the greater the impact on the cell’s overall potential. As they are directly involved in the transfer of charge.
Absolutely, the calculator is an excellent resource for educators and students. Providing a clear, practical tool for understanding and applying the principles of electrochemistry.