The Expiratory Reserve Volume Calculator is designed to estimate the volume of air that can still be expelled from the lungs after a normal exhalation. This measurement is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring conditions affecting lung elasticity and strength. It is particularly useful for athletes, patients with respiratory issues, and healthcare providers managing such patients.
Formula of Expiratory Reserve Volume Calculator
The formula used by the calculator is straightforward:
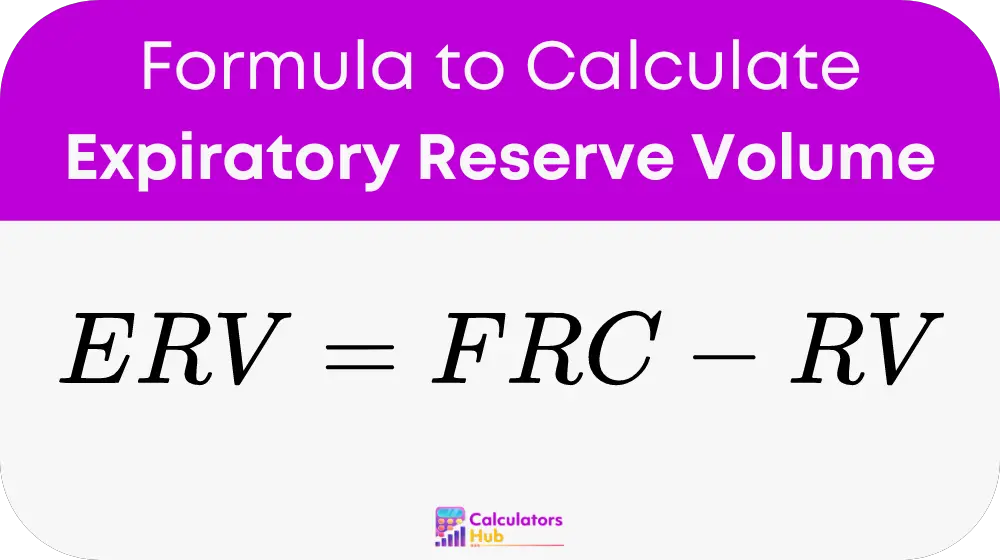
where:
- ERV stands for Expiratory Reserve Volume, indicating the extra air exhaled during a forceful breath out.
- FRC is the Functional Residual Capacity, the air remaining in the lungs after a normal exhalation.
- RV refers to the Residual Volume, the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal exhalation.
Understanding these components helps in accurately assessing lung function and potential respiratory issues.
General Terms and Conversion Table
To aid in understanding and using the calculator, here is a table of commonly used respiratory terms and conversions:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| ERV | Expiratory Reserve Volume |
| FRC | Functional Residual Capacity |
| RV | Residual Volume |
These terms are essential for interpreting results from the calculator and for applying them to real-life assessments or medical records.
Example of Expiratory Reserve Volume Calculator
Consider a scenario where a patient has an FRC of 2.5 liters and an RV of 1.2 liters. Using the calculator: ERV = 2.5 - 1.2 = 1.3 liters. This result can help in diagnosing or monitoring conditions like COPD or asthma, where such measurements are critical.
Most Common FAQs
Expiratory Reserve Volume is the additional air that can be forcibly exhaled after the end of a normal expiration.
Knowing your ERV can assist in monitoring lung health, diagnosing respiratory conditions, and assessing the impact of fitness or rehabilitation programs on lung capacity.
ERV, FRC, and RV are different components of lung volumes measure to assess various aspects of lung health and capacity. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate medical assessment and treatment.