The Attack Rate Calculator quantifies the proportion of individuals in a population who develop a disease during a specific time frame. This metric is vital for understanding the severity and spread of an outbreak, helping public health officials make informed decisions about necessary interventions.
Formula of Attack Rate Calculator
The formula for calculating the attack rate is:
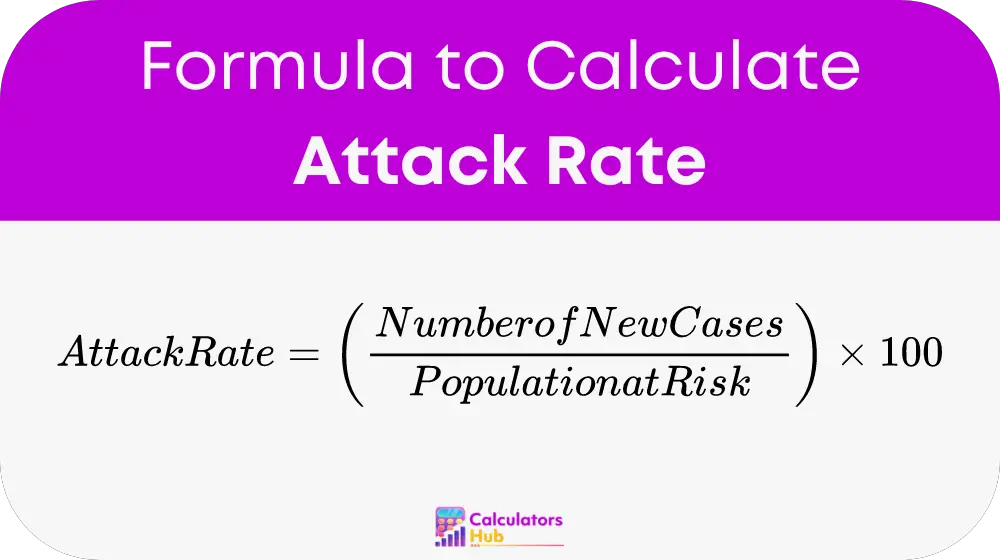
This involves:
- Number of New Cases: Refers to the count of new instances of the disease identified within the defined period.
- Population at Risk: The total number of individuals susceptible to the disease in the population during the same timeframe.
Table for General Usage
The following table provides pre-calculated attack rates for hypothetical scenarios, facilitating a quick reference for professionals without needing to perform manual calculations each time:
| Condition | Population at Risk | New Cases | Attack Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disease A | 1,000 | 50 | 5.0 |
| Disease B | 500 | 25 | 5.0 |
| Disease C | 2,000 | 300 | 15.0 |
This table allows users to estimate attack rates rapidly, comparing different conditions or outbreaks.
Example of Attack Rate Calculator
Consider a small community facing an outbreak where 500 individuals were at risk, and 25 developed the condition over the month. Using the Attack Rate Calculator:
Attack Rate = (25 / 500) * 100 = 5%
This result shows a relatively low attack rate, suggesting that while the disease is present, it may not be highly infectious or widespread, depending on additional factors such as disease type and community immunity.
Most Common FAQs
A1: Knowing the attack rate helps public health officials gauge the intensity of an outbreak and determine necessary control measures.
A2: Yes, attack rates can significantly vary depending on the disease's infectiousness and the population's characteristics. Such as age, immunity, and density.
A3: Ensure accurate and timely data collection on new cases and population demographics. Employ consistent methods for case identification and population assessment to maintain data integrity.