The Resultant Calculator is a useful tool used to find the resultant of two or more vectors. It helps determine the combined effect or magnitude of multiple forces acting simultaneously in different directions. This tool is valuable in various fields, including physics, engineering, and mathematics, where understanding the net effect of multiple vectors is crucial for analysis and problem-solving.
Formula of Resultant Calculator
The formula to calculate the resultant of two or more vectors is:
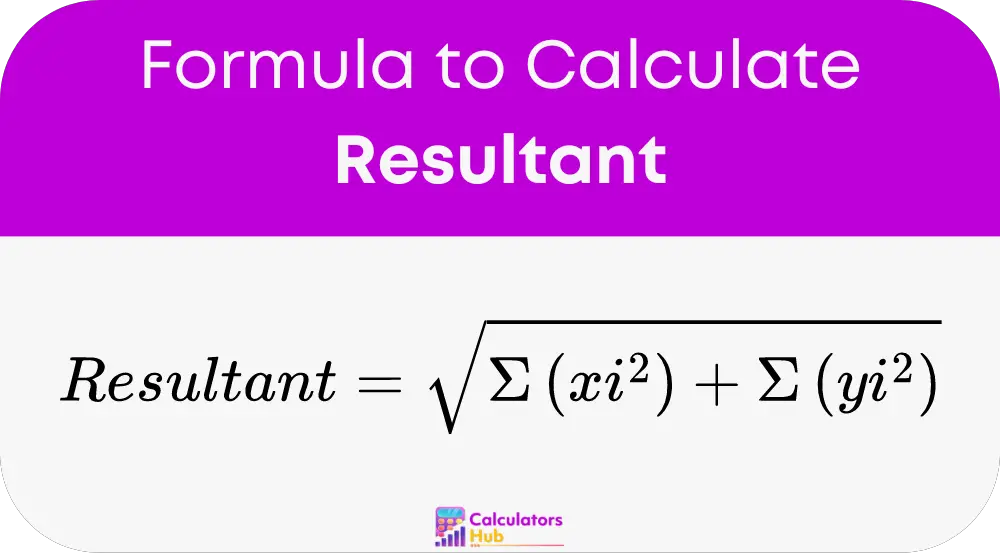
Where:
- xi represents the x-component of each vector.
- yi represents the y-component of each vector.
- n is the total number of vectors.
General Terms Table
To assist users in understanding and utilizing the Resultant Calculator effectively, here’s a table of general terms commonly associated with vector calculations:
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | The size or length of a vector. |
| Direction | The angle or orientation of a vector. |
| Vector Addition | The process of combining vectors to find the resultant. |
Example of Resultant Calculator
Let’s consider an example to illustrate how the Resultant Calculator works in practice:
Suppose we have two vectors:
- Vector A with components x_A = 3 and y_A = 4.
- Vector B with components x_B = -2 and y_B = 6.
Using the Resultant Calculator, we can find the resultant as follows:
resultant = √((3^2 + (-2)^2) + (4^2 + 6^2))
resultant = √65 ≈ 8.06
So, the resultant of Vector A and Vector B is approximately 8.06.
Most Common FAQs
A: Simply input the x and y components of each vector into the designated fields, then click the “Calculate” button to find the resultant.
A: Yes, the Calculator can handle any number of vectors. Simply add the x and y components of each vector accordingly.
A: The Resultant Calculator provides the resultant in the same units as the input vectors. Ensure consistency in units for accurate results.