Historically, the “Half Your Age Plus 7” rule emerged in the early 20th century, serving as a crude heuristic embedded in the social fabric of Western societies. It was popularized through literature and film, reflecting societal attitudes towards age differences in romantic partnerships. The rule implies a formula that helps individuals calculate the minimum age of a person they should date or marry, which ostensibly helps avoid social scrutiny or discomfort.
Formula of Half Your Age Plus 7 Calculator
The mathematical formula for this rule is straightforward yet powerful in its social implications:
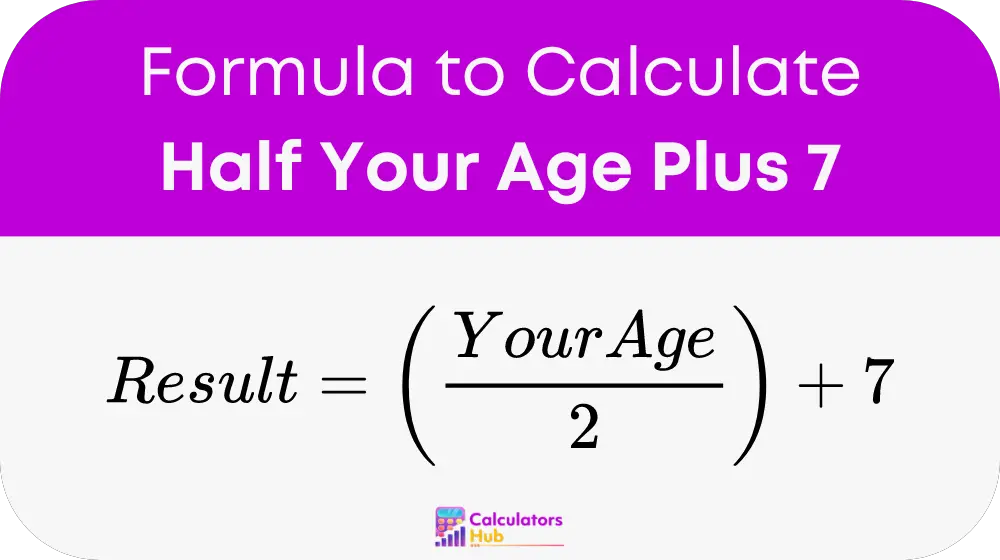
This formula calculates the minimum age of a partner that is considered socially acceptable for someone based on their own age.
Table for General Use
To simplify the application of this rule, below is an expanded table showing the minimum acceptable age of a partner for different ages, providing a quick reference:
| Your Age | Minimum Partner Age | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 14 | 14 | At the threshold of adolescence, the rule suggests dating peers. |
| 20 | 17 | Reflects caution as individuals enter early adulthood. |
| 30 | 22 | Demonstrates increasing acceptance of age gaps as individuals mature. |
| 40 | 27 | Indicates societal tolerance for wider age differences with age. |
| 50 | 32 | Further acceptance of significant age differences. |
| 60 | 37 | Highlights continued acceptance as individuals age. |
| 70 | 42 | At advanced ages, the formula still maintains a boundary for social acceptance. |
Example of Half Your Age Plus 7 Calculator
Consider a practical example to illustrate the rule: A person who is 40 years old would calculate the minimum age of their potential partner as follows:
Result = (40) / 2 + 7 = 27
This calculation indicates that a 40-year-old dating someone younger than 27 may face social judgments or discomfort.
Most Common FAQs
While widely recognized, the “Half Your Age Plus 7” rule varies significantly across different cultures and personal beliefs. It serves more as a guideline rather than a strict rule.
This rule should be considered as a guideline within the context of social norms but not as a hard-and-fast rule for making significant life decisions.
Yes, exceptions often arise based on individual circumstances, maturity levels, and cultural factors which might influence relationship dynamics differently.