The Flame Speed Calculator helps estimate how fast a flame moves through a gas mixture during combustion. This is useful in areas like engine design, fire safety, and fuel efficiency research. There are two types of flame speeds: laminar (smooth and steady) and turbulent (chaotic and fast). This calculator provides a way to estimate both.
Formula of Flame Speed Calculator
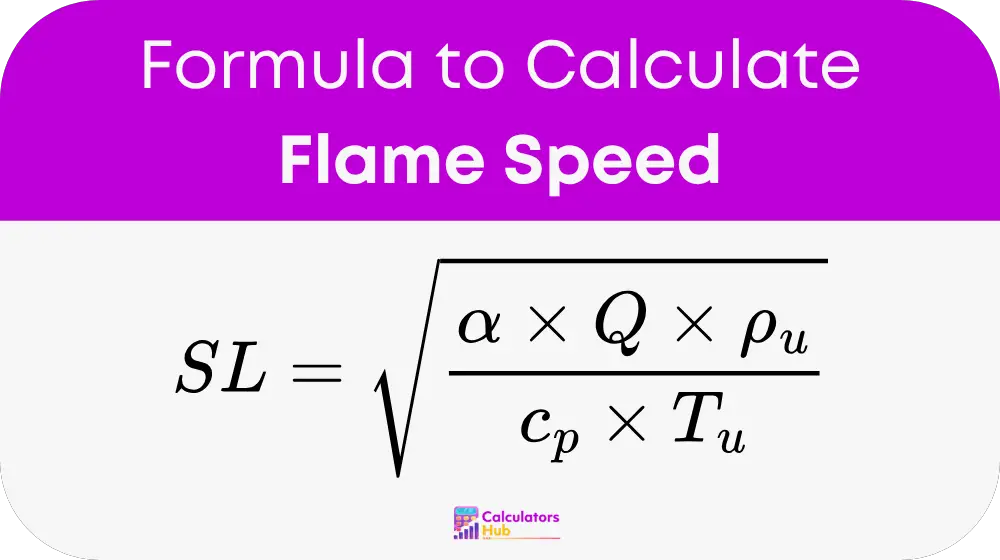
Where:
SL = Laminar flame speed in meters per second
α = Thermal diffusivity of the unburned gas in square meters per second
Q = Heat released per kilogram of fuel in joules
ρu = Density of the unburned gas in kilograms per cubic meter
cp = Specific heat at constant pressure in joules per kilogram kelvin
Tu = Temperature of the unburned gas in kelvin
For turbulent flame speed:
Turbulent Flame Speed (ST) = SL × (1 + u prime divided by SL) to the power of n
Where:
u prime = Turbulence intensity in meters per second
n = Constant value, usually between 0.5 and 1.0
Common Terms and Reference Table
This table gives typical values people search for and use when they do not have their own measurements.
| Fuel Type | Laminar Flame Speed (m/s) | Heat Release Q (J/kg) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Methane | 0.38 | 50000000 | Used in natural gas |
| Propane | 0.46 | 46400000 | Common in burners |
| Hydrogen | 2.90 | 120000000 | Very fast flame speed |
| Ethanol | 0.40 | 29700000 | Alcohol-based fuel |
| Gasoline | 0.40 | 44000000 | Internal combustion engines |
Example of Flame Speed Calculator
Suppose you want to calculate the flame speed for methane. Use the following values:
alpha = 0.000022
Q = 50000000
rho_u = 0.65
cp = 1005
Tu = 300
Insert into the formula:
SL = square root of (0.000022 × 50000000 × 0.65) divided by (1005 × 300)
SL = square root of (715000) divided by 301500
SL = square root of 2.37
SL is approximately 1.54 meters per second
Most Common FAQs
Answer: It is the rate at which a flame travels through a gas mixture during burning. It helps in understanding how a fuel burns.
Answer: It helps researchers and engineers design safer and more efficient combustion systems, such as engines and industrial burners.
Answer: Yes, but the liquid must be converted into gas or vapor first. The flame speed is calculated based on gas-phase combustion.