The Accident Frequency Rate Calculator is design to calculate the AFR, which is the number of work-related accidents per one million hours worked. This calculator helps organizations assess their safety performance, identify areas for improvement, and implement necessary safety measures. By using the AFR Calculator, companies can ensure they are taking proactive steps to reduce workplace accidents and promote a culture of safety.
Formula of Accident Frequency Rate Calculator
The Accident Frequency Rate (AFR) is calculate using the following formula:
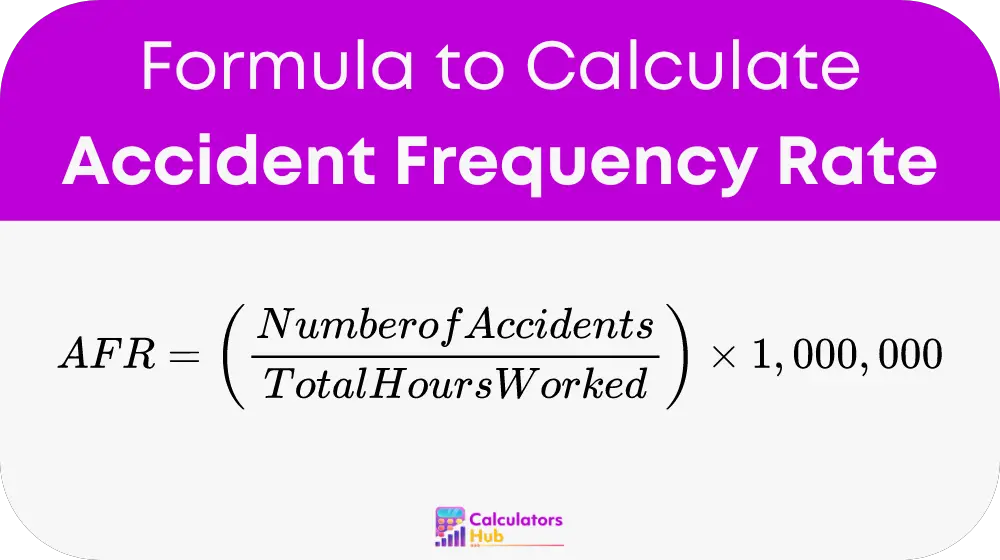
Where:
- Number of Accidents is the total count of work-related accidents.
- Total Hours Worked is the cumulative number of hours worked by all employees.
- The factor 1,000,000 is use to normalize the AFR to a standard base of one million hours worked.
General Terms and Useful Conversions
Here is a table of general terms and common conversions related to AFR, which can be helpful for quick reference:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Number of Accidents | Total count of work-related accidents |
| Total Hours Worked | Cumulative number of hours worked by all employees |
| Normalization Factor | Standard base of one million hours worked |
| AFR | Accident Frequency Rate |
Example of Accident Frequency Rate Calculator
To illustrate the use of the AFR formula, let's consider a practical example:
Example: A company has reported 5 work-related accidents over a period where employees have collectively worked 2,000,000 hours. Using the AFR formula:
AFR = (5 / 2,000,000) * 1,000,000
AFR = 2.5
This means the company's Accident Frequency Rate is 2.5 accidents per one million hours work.
Most Common FAQs
A good AFR value varies by industry, but generally, a lower AFR indicates better safety performance. Organizations should aim for a value as close to zero as possible.
AFR should be calculate regularly, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis, to monitor trends and identify any areas requiring immediate attention.
To improve AFR, companies should implement comprehensive safety training, conduct regular safety audits, encourage reporting of near-misses, and continuously improve safety protocols.