The Energy Per Symbol Calculator helps users determine how much energy is used to transmit a single symbol in a digital communication system. It is an essential measurement in telecommunications, especially when analyzing power efficiency, bandwidth usage, and overall system performance. This metric plays a key role in designing modems, wireless networks, satellite links, and optical systems. The calculator belongs to the Digital Communication Calculator category.
By calculating energy per symbol, engineers can compare transmission schemes, evaluate noise tolerance, and optimize energy use in power-limited or bandwidth-sensitive applications.
Formula of Energy Per Symbol Calculator
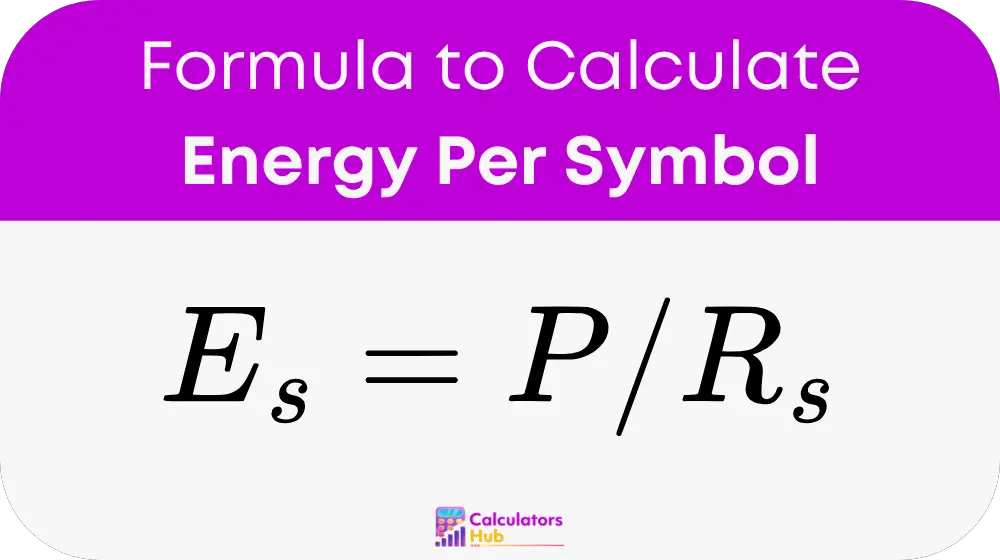
Detailed Breakdown:
Eₛ = Energy per symbol (in joules)
P = Average transmit power (in watts)
Rₛ = Symbol rate (in symbols per second, also called baud rate)
The formula assumes continuous and consistent transmission power. It measures how much energy is allocated to each symbol sent over the channel.
Quick Reference Table
The following table includes values that represent commonly used transmission settings. This helps users estimate energy per symbol without manually computing for every case.
| Average Power (W) | Symbol Rate (symbols/sec) | Energy per Symbol (J) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1000 | 0.001 |
| 2 | 2000 | 0.001 |
| 0.5 | 1000 | 0.0005 |
| 1.5 | 3000 | 0.0005 |
| 3 | 6000 | 0.0005 |
This table shows that as symbol rate increases, energy per symbol decreases if the power remains constant. It also highlights the trade-off between speed and energy efficiency.
Example of Energy Per Symbol Calculator
Let’s say a communication system transmits at an average power of 2 watts and uses a symbol rate of 2000 symbols per second.
Step 1:
Use the formula
Eₛ = P / Rₛ
Eₛ = 2 / 2000 = 0.001 joules per symbol
So, each transmitted symbol uses 0.001 joules of energy.
Most Common FAQs
It helps evaluate how much energy is needed to send information, which is useful for optimizing battery life and reducing power consumption in digital communication systems.
No. Symbol rate is the number of symbols transmitted per second, while bit rate depends on how many bits are encoded per symbol. For example, 1 symbol may carry 2, 4, or more bits depending on the modulation.
Yes. It works for both wired and wireless systems, including Wi-Fi, 5G, satellite links, and optical fibers.