The dBi to dBm calculator is an invaluable tool for anyone involved in the design, installation, or maintenance of wireless communication systems. It converts the antenna gain, measured in dBi (decibels relative to an isotropic radiator), into dBm (decibels relative to one milliwatt), thus providing a clearer picture of the effective radiated power of an antenna. This conversion is pivotal for assessing the strength of a signal that an antenna can emit or receive, facilitating the optimization of wireless networks for enhanced performance and reliability.
Formula of dBi to dBm Calculator
The essence of the dBi to dBm calculator lies in its formula, a straightforward yet powerful expression that translates theoretical gain into practical output power. Here's how it works:
Identify the Radiated Power (P): Begin with the radiated power of the antenna, usually specified in watts (W) or milliwatts (mW). This figure is often found in the antenna's technical datasheet.
Apply the dBm Conversion Formula:
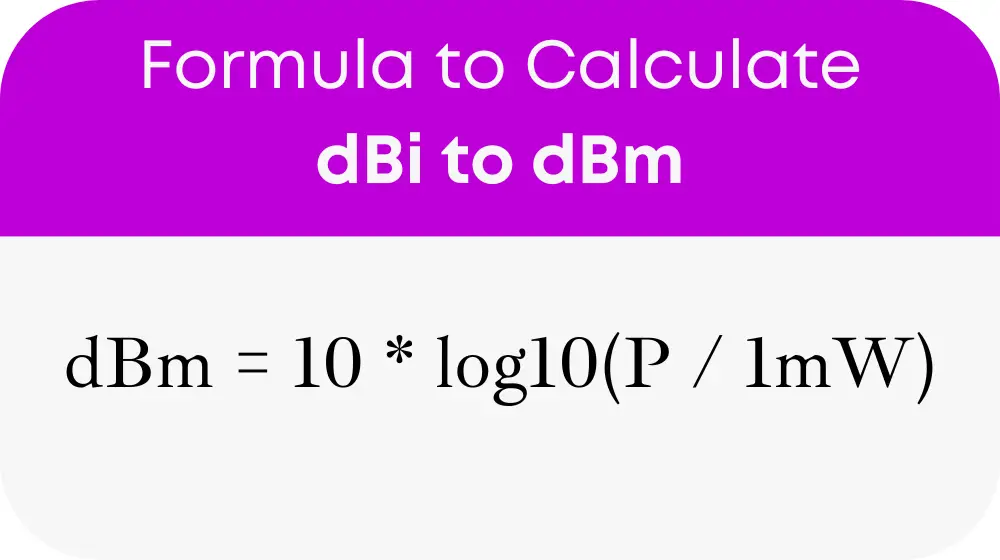
This formula converts the radiated power (P) in milliwatts into dBm, offering a standardized measure of power output relative to 1 milliwatt. It serves as the foundation for understanding and using the dBi to dBm calculator effectively.
Table for General Terms
| Term | Definition | Example/Usage |
|---|---|---|
| dBm | A unit of power expressed in decibels relative to one milliwatt. It quantifies signal strength. | A signal of 0 dBm equals 1 mW of power. |
| dBi | Decibels relative to an isotropic radiator, a measure of antenna gain that indicates how much power is directed in a specific direction compared to an isotropic antenna. | An antenna with 3 dBi gain doubles the effective power in its favored direction. |
| Radiated Power (P) | The actual power emitted by an antenna, usually specified in milliwatts (mW). | An antenna radiating 50 mW of power. |
| Conversion Formula | The formula used to convert radiated power (P) in mW to dBm. | dBm = 10 * log10(P / 1mW) |
| Effective Radiated Power | The power level, expressed in dBm, indicating the combination of the transmitter power and the antenna gain. | Calculated using the dBm conversion formula. |
Example of dBi to dBm Calculator
Let's elucidate the formula with a practical example. Consider an antenna with a radiated power of 50 mW. To convert this power into dBm:
- Calculate: dBm = 10 * log10(50 / 1) = 17 dBm
This result indicates that the antenna's effective radiated power, in terms of dBm, is 17 dBm, providing a quantifiable measure of the antenna's output.
Most Common FAQs
dBi measures antenna gain relative to an isotropic radiator, while dBm indicates power output relative to one milliwatt. dBi reflects efficiency and directionality, whereas dBm quantifies signal strength.
This conversion helps in understanding the effective power an antenna can emit, aiding in system design and performance optimization. It translates antenna efficiency into actual output, essential for network planning.
Antenna gain (dBi) amplifies the signal strength without physically increasing the power input. Higher gain results in stronger signal output (dBm), improving communication range and quality.