A D Prime (d') Calculator is a tool used in signal detection theory to measure sensitivity in distinguishing between signal and noise. It quantifies an observer's ability to detect a stimulus amidst background noise, making it useful in fields like psychology, neuroscience, sensory processing, and machine learning.
By using this calculator, professionals can:
- Assess perceptual sensitivity in experiments.
- Evaluate the performance of detection systems.
- Analyze cognitive and sensory decision-making processes.
- Compare observer performance across different conditions.
A higher d' value indicates better discrimination between signal and noise, while a lower value suggests difficulty in distinguishing between the two.
Formula of D Prime Calculator
The formula for calculating D Prime (d') is:
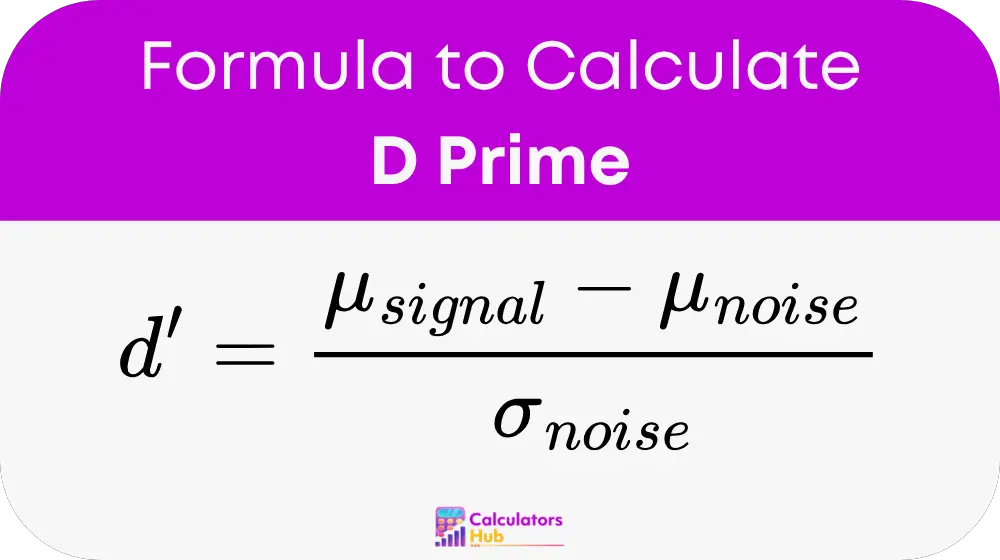
Where:
- μ_signal is the mean of the signal distribution (e.g., the mean of the signal-present trials).
- μ_noise is the mean of the noise distribution (e.g., the mean of the signal-absent trials).
- σ_noise is the standard deviation of the noise distribution.
In simpler terms, d' represents the distance between the means of the signal and noise distributions, normalized by the standard deviation of the noise. A larger d' indicates greater sensitivity in distinguishing signals from noise.
D Prime Reference Table
Below is a table that provides a general interpretation of d' values to help users quickly understand their results.
| d' Value | Sensitivity Level | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | No Sensitivity | Complete overlap between signal and noise. |
| 0.5 | Low Sensitivity | Weak ability to distinguish signal from noise. |
| 1.0 | Moderate Sensitivity | Somewhat clear differentiation between signal and noise. |
| 2.0 | High Sensitivity | Strong ability to detect signal amidst noise. |
| 3.0+ | Very High Sensitivity | Nearly perfect discrimination of signal from noise. |
This table provides a simple guide for interpreting d' scores in various contexts.
Example of D Prime Calculator
Let’s assume an experiment measures the ability to detect a tone in background noise. The recorded values are:
- μ_signal = 10
- μ_noise = 4
- σ_noise = 2
Using the formula:
d' = (10 - 4) / 2 d' = 6 / 2 d' = 3.0
This result suggests very high sensitivity, meaning the observer can reliably differentiate between signal and noise.
Most Common FAQs
D prime is crucial because it quantifies how well an observer or system can distinguish between signal and noise, making it useful in psychological testing, machine learning, and decision-making analysis.
No, d' values are generally non-negative since they represent a distance measurement. However, incorrect data input or reversed signal/noise conditions might produce misleading results.
Increasing signal clarity, reducing background noise, and optimizing detection strategies can improve d'. In experimental settings, adjusting stimulus intensity or using training methods may enhance sensitivity.