The Array Gain Calculator is designed to help in calculating the gain of an antenna array, which is the increase in signal strength and directivity when multiple antennas are used together compared to a single antenna. This calculator simplifies the complex calculations involved in antenna array design, enabling users to quickly determine the optimal number of elements to achieve the desired gain.
Formula of Array Gain Calculator
The formula to calculate the gain of an antenna array in decibels (dB) is:
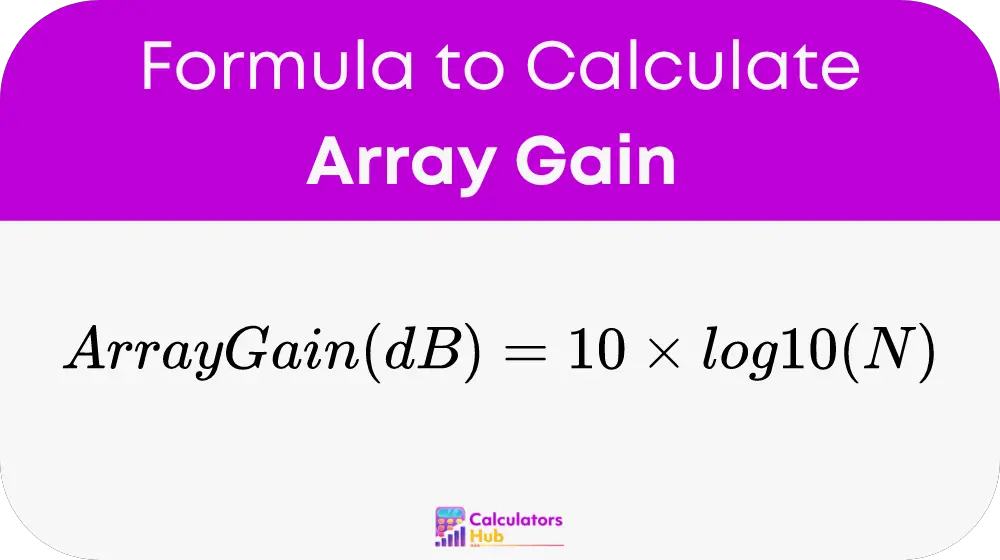
Where:
- N is the number of elements in the array.
This formula quantifies the gain in terms of decibels, offering a clear measurement of how much the signal strength is amplified by the array configuration.
Table of General Terms
For the convenience of users, here’s a table of general terms related to the Array Gain Calculator:
| Term | Description | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| Array Gain (dB) | Gain of the antenna array in decibels | 10 dB, 20 dB |
| Number of Elements | Number of antennas in the array | 2, 4, 8, 16 |
Example of Array Gain Calculator
For instance, if an antenna array consists of 16 elements, the array gain can be calculated as follows:
Array Gain (dB) = 10 × log10(16) = 12 dB
This calculation shows that using 16 antennas in an array configuration results in a gain of 12 dB, significantly enhancing the signal strength compared to a single antenna.
Most Common FAQs
A1: Increasing the number of elements generally increases the array gain logarithmically. More elements lead to higher directivity and better signal focusing, thus amplifying the received or transmitted signal.
A2: Yes, while adding more elements does increase the gain, the rate of gain increase decreases as the number of elements grows. The physical arrangement and interaction between elements also play a critical role.
A3: The calculator is applicable to any antenna type as long as it is part of an array configuration. However, specific characteristics of different antenna types may affect the overall array performance.