The Antenna Reflector Size Calculator is an essential tool for engineers and technicians in the field of telecommunications and radio frequency (RF) engineering. This calculator helps determine the optimal size of a reflector for an antenna, which is crucial for enhancing signal strength, improving directionality, and minimizing interference. Accurate reflector sizing ensures that antennas operate at peak efficiency, providing reliable and high-quality communication.
Formula of Antenna Reflector Size Calculator
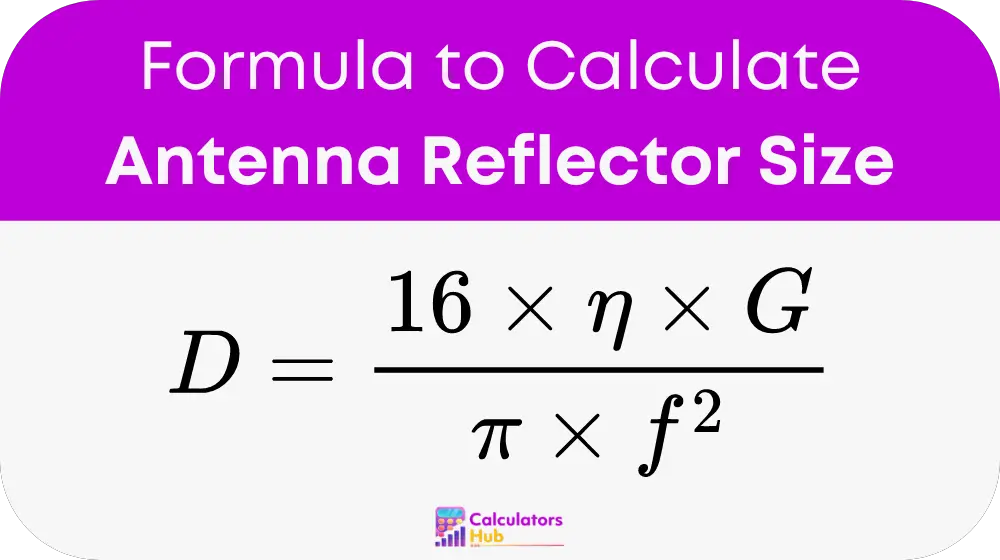
To calculate the diameter of an antenna reflector, the following formula is used:
Detailed Explanation
- D: Diameter of the reflector in meters (m).
- η: Efficiency of the antenna (ratio, not percentage).
- G: Gain of the antenna in linear scale.
- π: Mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
- f: Frequency of the signal in hertz (Hz).
Steps for Calculation
- Convert the gain from dBi to linear scale:
- G_linear = 10^(G_dBi / 10)
- Determine the efficiency (η): Efficiency is typically provided by the antenna manufacturer.
- Obtain the frequency (f): Frequency at which the antenna operates.
- Plug these values into the formula to calculate the reflector diameter (D).
General Reference Table
Here's a table to help understand how changes in gain and frequency affect the size of the antenna reflector:
| Gain (dBi) | Frequency (GHz) | Efficiency (η) | Reflector Diameter (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 2.4 | 0.6 | 2.02 |
| 35 | 5.0 | 0.7 | 1.14 |
| 40 | 10.0 | 0.8 | 0.64 |
| 45 | 15.0 | 0.9 | 0.42 |
This table illustrates how higher frequencies or lower gains result in smaller reflector sizes, emphasizing the importance of accurate calculations for optimal performance.
Example of Antenna Reflector Size Calculator
Consider an antenna operating at a frequency of 3 GHz, with a gain of 25 dBi and an efficiency of 0.75. Using the formulas provided:
- Convert dBi to linear gain:
- G_linear = 10^(25 / 10) ≈ 316.23
- Calculate the reflector diameter:
- D = (16 * 0.75 * 316.23) / (π * (3 * 10^9)^2)
- D ≈ 0.067 meters
This example demonstrates that at a frequency of 3 GHz with a gain of 25 dBi, the optimal reflector diameter is approximately 0.067 meters.
Most Common FAQs
A reflector enhances the antenna's signal strength and directionality by reflecting electromagnetic waves, thereby increasing the effective gain and improving overall performance.
Higher frequencies result in smaller reflector sizes, while lower frequencies require larger reflectors to achieve the same performance.
Yes, improving the design, using higher-quality materials, and optimizing the installation can enhance antenna efficiency, leading to better performance.