The Antenna Dbi Range Calculator is an indispensable tool for radio frequency (RF) engineers and communications professionals who need to estimate the effective communication range of an antenna system. This calculator not only simplifies the complex calculations involved in determining transmission range but also enables accurate system planning and optimization for various communication scenarios.
Formula of Antenna Dbi Range Calculator
To calculate the range of an antenna, we use the following comprehensive formula:
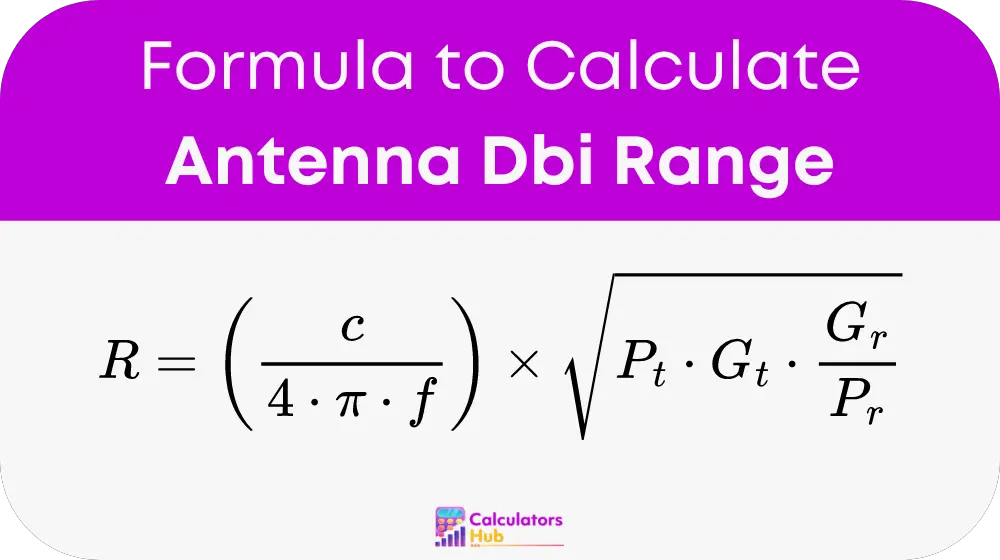
Detailed Breakdown of Terms:
- R: Range in meters.
- c: Speed of light in a vacuum, approximately 3 * 10^8 meters per second.
- f: Frequency in hertz (Hz).
- P_t: Transmit power in watts (W).
- G_t: Transmit antenna gain in linear scale.
- G_r: Receive antenna gain in linear scale.
- P_r: Receiver sensitivity in watts (W).
For converting antenna gain from dBi (decibels relative to isotropic) to a linear scale, use:
G_linear = 10^(G_dBi / 10)
Interpretation:
- G_linear: Antenna gain in linear scale.
- G_dBi: Antenna gain in dBi.
This calculation provides a clear estimate of how far a signal can effectively travel, considering the power of the transmitter, the sensitivity of the receiver, and the gains of both the transmitting and receiving antennas.
General Reference Table
Here’s a table to help quickly convert dBi to linear gain, which is often needed when using the range calculator:
| Antenna Gain (dBi) | Linear Gain (G_linear) |
|---|---|
| 0 dBi | 1 |
| 3 dBi | 2 |
| 6 dBi | 4 |
| 9 dBi | 8 |
| 12 dBi | 16 |
Example of Antenna Dbi Range Calculator
Consider a scenario where you want to calculate the communication range of an RF system operating at 2 GHz, with a transmitter power of 50 watts, a transmit antenna gain of 14 dBi, a receive antenna gain of 14 dBi, and a receiver sensitivity of 0.0001 watts:
-
Convert dBi to linear scale:
- G_t = G_r = 10^(14 / 10) = 25.12
-
Calculate the range:
- R = (3 * 10^8 / (4 * π * 2 * 10^9)) * √(50 * 25.12 * 25.12 / 0.0001) ≈ 81,106 meters
This example demonstrates how the calculator can be used to predict the effective range of a communication system under specified conditions.
Most Common FAQs
Environmental conditions, antenna placement, and obstructions can significantly affect the actual range, despite theoretical calculations.
Improving the transmit power, using higher gain antennas, and optimizing antenna placement can enhance the communication range.
Yes, the calculator is versatile and can be used for any frequency, provided that the appropriate input values are given.