This tool computes the probability density function for various types of data distributions, notably the normal (Gaussian) distribution. It is vital for statisticians, researchers, and anyone involved in data analysis, helping to visualize and calculate the probability of different outcomes in a dataset.
Formula of PDF Function Calculator
The formula for the probability density function of a normal distribution is:
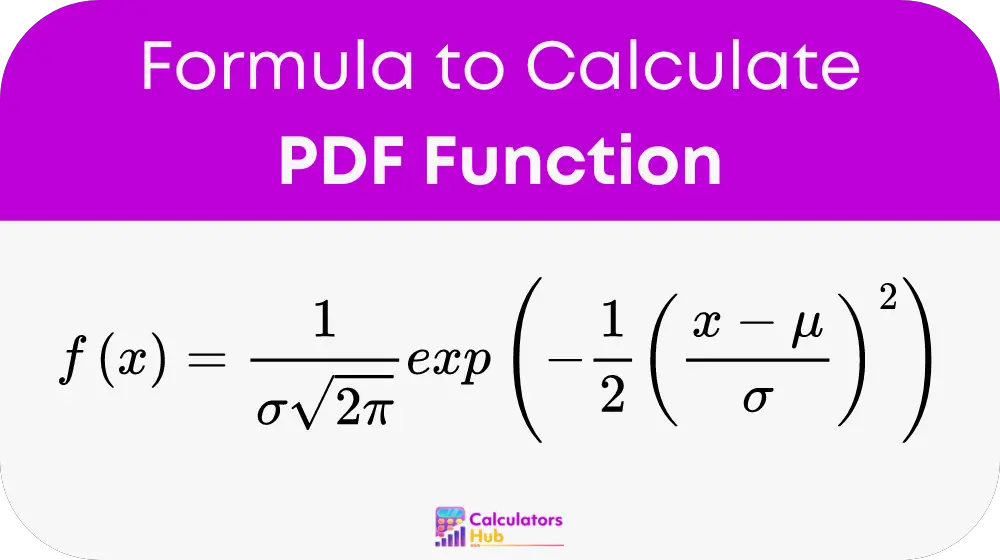
where:
- x is the value for which the PDF is calculated,
- μ (mu) is the mean,
- σ (sigma) is the standard deviation,
- π is Pi (approximately 3.14159),
- exp denotes the exponential function.
This formula is crucial for determining the distribution curve’s shape, which shows how likely different outcomes are.
Table for General Terms
| Term | Symbol | Importance in PDF Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | μ | Central value around which data is distributed |
| Standard Deviation | σ | Indicates how data spreads around the mean |
| Variance | σ^2 | Squared standard deviation |
This table helps users grasp key statistical terms and their importance in PDF calculations.
Example of PDF Function Calculator
Consider data with a mean (μ) of 50 and a standard deviation (σ) of 10. Using the PDF Function Calculator, we find a higher probability of observing values around 50 compared to those far from the mean. This can be depicted through a bell-shaped curve, showing how data points are distributed.
Most Common FAQs
A PDF shows the distribution of values for a random variable, essential for predicting different outcomes.
It offers a quantitative and visual method to comprehend data distributions, crucial for testing hypotheses and making decisions.
While valuable, it requires precise data input and understanding of the distribution type for meaningful results.