The Differential Coefficient Calculator is a tool designed to compute the derivative of a function with respect to a given variable. It helps users determine the rate at which a function changes at any given point. This is particularly useful in calculus, physics, engineering, and economics, where differentiation is applied to analyze motion, optimization, and rate-related problems. By entering a function, users can quickly compute its derivative without manual calculations.
Formula of Differential Coefficient Calculator
The differential coefficient, or derivative, of a function f(x) with respect to x is given by:
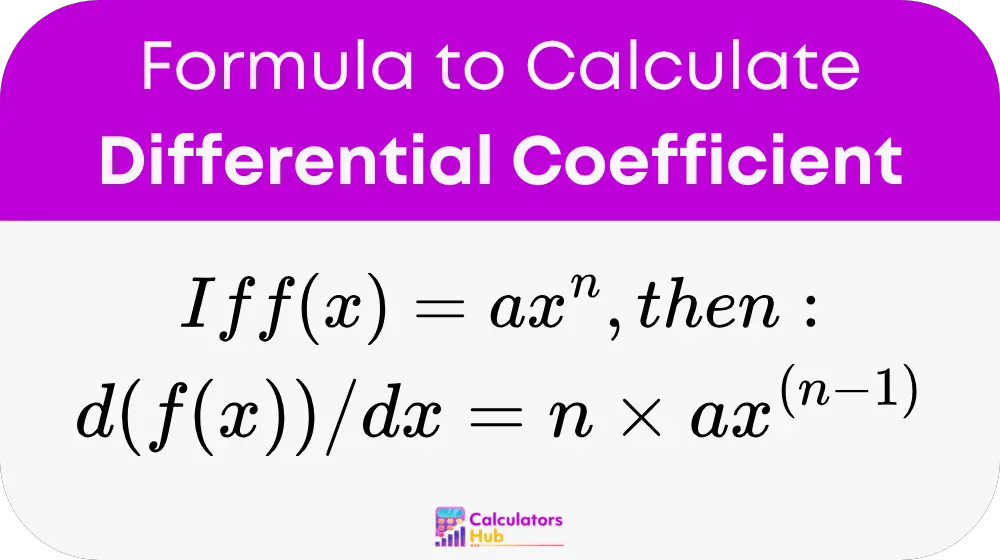
where:
- f(x) is the function to be differentiate.
- x is the variable with respect to which differentiation is perform.
- a is a constant coefficient.
- n is the exponent of the variable.
Common Derivatives:
- d(x^n) / dx = n * x^(n-1)
- d(e^x) / dx = e^x
- d(ln x) / dx = 1/x
- d(sin x) / dx = cos x
- d(cos x) / dx = -sin x
The calculator applies these and other differentiation rules to provide quick results.
Differential Coefficient Reference Table
This table provides derivatives of common functions to help users understand and apply differentiation more efficiently:
| Function | Derivative |
|---|---|
| x^n | n * x^(n-1) |
| e^x | e^x |
| ln(x) | 1/x |
| sin(x) | cos(x) |
| cos(x) | -sin(x) |
| tan(x) | sec^2(x) |
| sec(x) | sec(x)tan(x) |
| csc(x) | -csc(x)cot(x) |
| cot(x) | -csc^2(x) |
This reference table is useful for quick calculations and checking derivative results.
Example of Differential Coefficient Calculator
Find the derivative of the function f(x) = 5x^3.
Using the formula:
d(5x^3) / dx = 3 * 5x^(3-1) = 15x^2
Thus, the derivative of f(x) = 5x^3 is f'(x) = 15x^2.
Most Common FAQs
A differential coefficient, also known as a derivative, represents the rate of change of a function with respect to its variable. It is widely use in calculus to analyze function behavior.
Differentiation is use in various fields, including physics, engineering, economics, and optimization. It helps determine slopes, velocity, acceleration, and growth rates, making it essential for problem-solving and analysis.
Yes, the Differential Coefficient Calculator can compute higher-order derivatives by applying differentiation successively to the first derivative of a function.