A Critical Probability Calculator is a statistical tool used to determine the probability that a test statistic exceeds a given critical value under the null hypothesis. This is commonly used in hypothesis testing to assess whether an observed result is statistically significant. By calculating the critical probability (p-value), users can make informed decisions about rejecting or failing to reject a null hypothesis based on a chosen significance level.
This calculator is widely use in fields such as finance, medicine, engineering, and social sciences to analyze data and make data-driven decisions.
Formula of Critical Probability Calculator
The formula to calculate the critical probability (p-value) is:
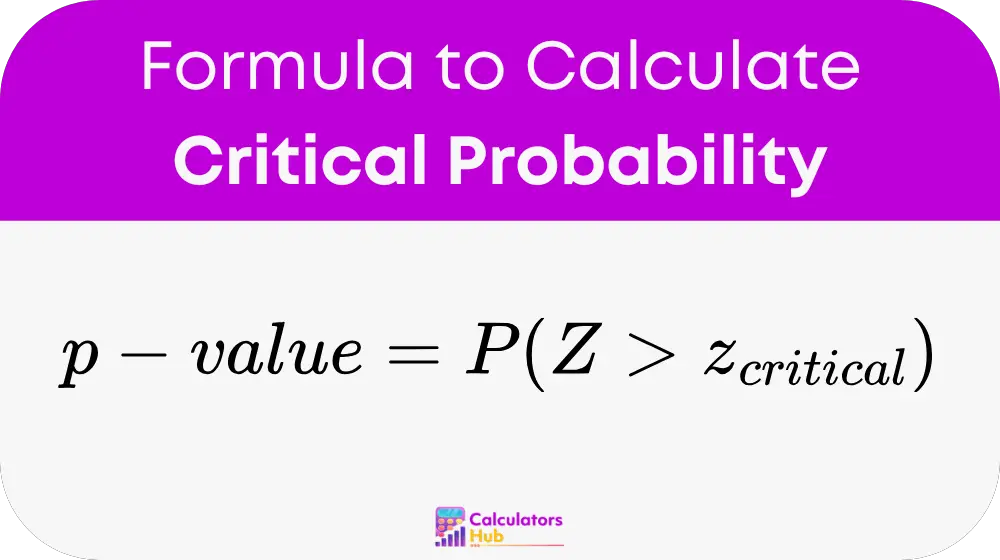
Where:
- Z is the z-score (or test statistic) corresponding to a sample data point.
- z_critical is the critical z-value that corresponds to the given significance level α (for a z-test or normal distribution).
- P(Z > z_critical) is the probability that the test statistic exceeds the critical value under the null hypothesis.
For a two-tailed test, the probability is computed as:
P(Z > |z_critical|) + P(Z < -|z_critical|)
The critical probability helps in determining whether to reject or retain the null hypothesis in a statistical test.
General Terms Table
Below is a reference table for common z-scores and their corresponding probability values for a standard normal distribution:
| Significance Level (α) | Critical z-value | p-value (One-tailed) | p-value (Two-tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 1.28 | 0.10 | 0.20 |
| 0.05 | 1.645 | 0.05 | 0.10 |
| 0.01 | 2.33 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| 0.001 | 3.09 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
This table provides an easy reference for critical values in hypothesis testing.
Example of Critical Probability Calculator
Let's consider an example where a researcher wants to test whether a new drug has a significant effect compared to a placebo. They use a standard normal distribution (z-test) with a significance level of 0.05.
Given:
- z_critical = 1.645 (for one-tailed test at α = 0.05)
- The test statistic calculated from the sample is Z = 2.10
To find the critical probability:
P(Z > 2.10) = 0.0179 (using a standard normal table)
Since the p-value (0.0179) is less than the significance level (α = 0.05), the null hypothesis is reject, meaning the drug has a statistically significant effect.
Most Common FAQs
The critical probability (p-value) is the likelihood that a test statistic falls in the rejection region of a hypothesis test under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. If the p-value is lower than the significance level (α), the null hypothesis is reject.
The critical value can be find using a standard normal distribution table (z-table) or statistical software. The critical z-value corresponds to the chosen α-level (e.g., 1.645 for α = 0.05 in a one-tailed test).
If the calculated p-value is lower than the chosen significance level (α), you reject the null hypothesis, indicating that the observed result is statistically significant. If the p-value is higher, you fail to reject the null hypothesis.