The Cohen’s D Calculator measures the effect size, which quantifies the difference between two groups. It is widely used in statistics, psychology, and social sciences to assess the practical significance of research findings. By calculating the standardized difference between two means, Cohen’s D helps researchers understand how large the difference is, independent of the sample size.
This tool is crucial for comparing experimental and control groups, evaluating treatment effectiveness, and analyzing data in various fields.
Formula of Cohen’s D Calculator
The formula for Cohen’s D is:
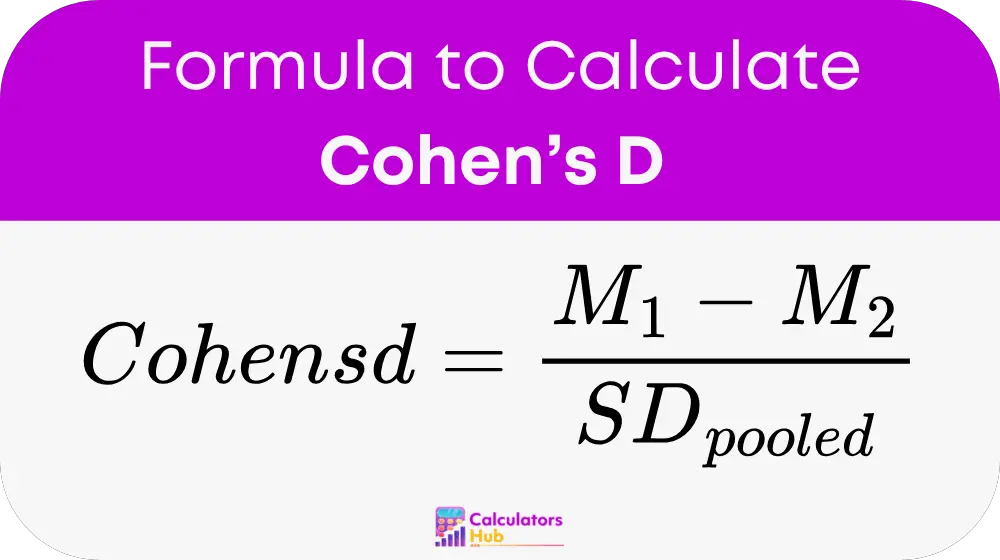
Where:
- M₁ is the mean of the first group.
- M₂ is the mean of the second group.
- SD_pooled is the pooled standard deviation.
Detailed Formulas for Variables
- Pooled Standard Deviation (SD_pooled):
SD_pooled = √[((n₁ - 1) × SD₁² + (n₂ - 1) × SD₂²) / (n₁ + n₂ - 2)]
Where:
- SD₁ is the standard deviation of the first group.
- SD₂ is the standard deviation of the second group.
- n₁ is the sample size of the first group.
- n₂ is the sample size of the second group.
- Standard Deviation for Each Group (if not provided):
SD = √[Σ(xᵢ - M)² / (n - 1)]
Where:
- xᵢ represents each individual value in the group.
- M is the mean of the group.
- n is the sample size of the group.
Table for Common Cohen’s D Values
| Cohen’s D Value | Effect Size Description | Practical Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | Small | Small difference between groups |
| 0.5 | Medium | Moderate difference between groups |
| 0.8 | Large | Large difference between groups |
| >1.0 | Very Large | Very substantial difference |
This table provides a general guideline for interpreting Cohen’s D values, helping users understand the magnitude of the effect.
Example of Cohen’s D Calculator
Let’s calculate Cohen’s D for two groups:
Group 1 (n₁ = 10): Mean (M₁) = 85, Standard Deviation (SD₁) = 10
Group 2 (n₂ = 10): Mean (M₂) = 70, Standard Deviation (SD₂) = 12
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Calculate Pooled Standard Deviation (SD_pooled):
SD_pooled = √[((10 - 1) × 10² + (10 - 1) × 12²) / (10 + 10 - 2)]
SD_pooled = √[2196 / 18] ≈ 11.05 - Calculate Cohen’s D:
Cohen’s d = (85 - 70) / 11.05
Cohen’s d ≈ 15 / 11.05 ≈ 1.36
Cohen’s D is approximately 1.36, indicating a very large effect size.
Most Common FAQs
Cohen’s D measures the effect size, helping researchers understand the practical significance of differences between two groups.
Yes, Cohen’s D can be negative, indicating the direction of the effect. However, the magnitude (absolute value) represents the effect size.
While Cohen’s D can be calculated for any sample size, larger sample sizes provide more reliable estimates and minimize the impact of variability.