The Binomial Variance Calculator is an invaluable tool for statisticians, students, and professionals involved in data analysis. It automates the computation of variance in a binomial distribution, saving time and reducing the potential for error. This calculator helps users understand the spread of data in experiments where outcomes are classified into two categories, such as success and failure.
Formula of Binomial Variance Calculator
The formula to calculate the variance of a binomial distribution is:
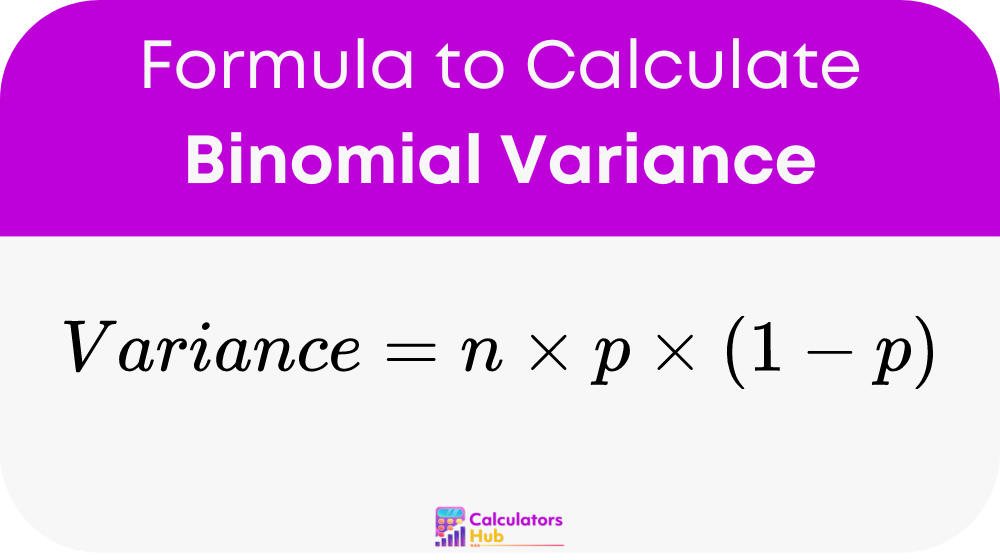
Where:
nis the number of trialspis the probability of success on each trial (expressed as a decimal)
This formula quantifies how much the number of successful outcomes can vary from one series of trials to another.
General Terms and Table
To better utilize the Binomial Variance Calculator, here are some key terms:
- Trial: An individual instance of an experiment.
- Success: The outcome of interest in a trial.
- Probability of Success (p): The likelihood of a success in a single trial.
| Number of Trials (n) | Probability of Success (p) | Variance |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 5.0 |
| 30 | 0.5 | 7.5 |
This table provides quick reference values that help in predicting outcomes without individual calculations.
Example of Binomial Variance Calculator
Consider a scenario where a coin is flip 10 times, and we want to find the variance in the number of heads. Assuming the probability of flipping a head (p) is 0.5, the variance would be calculated as follows:
Variance = 10 × 0.5 × (1−0.5) = 2.5
This indicates that the number of heads can vary, on average, by 2.5 from the expected outcome.
Most Common FAQs
A1: A higher variance indicates a greater spread around the expected number of successes, implying less predictability in the outcomes.
A2: Yes, as long as the trials are independent and the outcome binary, the calculator is applicable.
