The Absolute Risk Reduction Calculator is designed to calculate the absolute difference in risk between two groups: a control group and an experimental group. ARR is a measure of how much a treatment reduces the risk of a negative outcome compared to a control group. This calculator is essential in clinical trials, epidemiological studies, and healthcare decision-making.
Formula of Absolute Risk Reduction Calculator
To calculate Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) accurately, the formula incorporates the size of the sample groups. The detailed formula is:
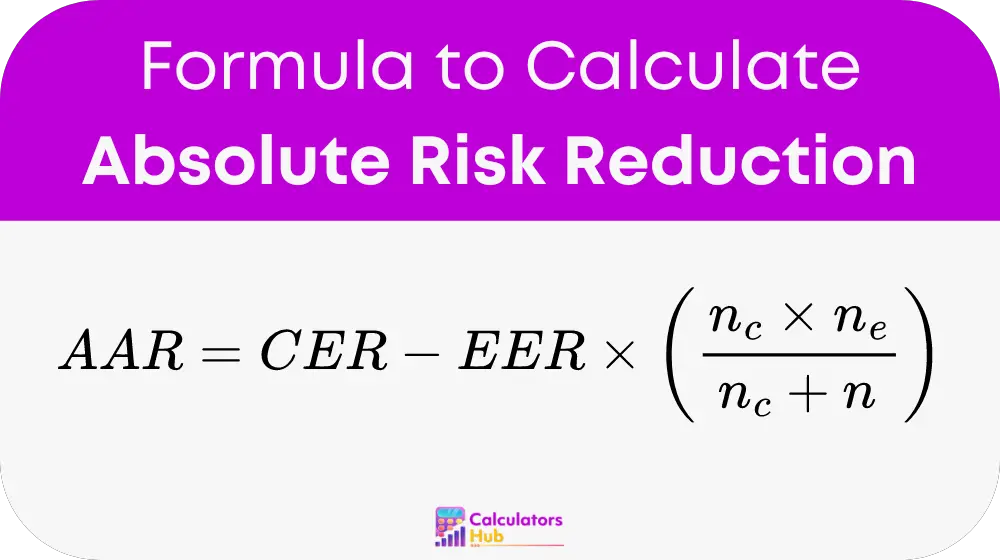
where:
- ARR: Absolute Risk Reduction
- CER: Control Event Rate
- EER: Experimental Event Rate
- n_c: Number of subjects in the control group
- n_e: Number of subjects in the experimental group
Definitions:
- Control Event Rate (CER): The proportion of patients in the control group who experience the event.
- Experimental Event Rate (EER): The proportion of patients in the experimental group who experience the event.
- Number of subjects in the control group (n_c)
- Number of subjects in the experimental group (n_e)
Table of General Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Absolute Risk Reduction | The difference in event rates between control and experimental groups |
| Control Event Rate (CER) | Proportion of events in the control group |
| Experimental Event Rate (EER) | Proportion of events in the experimental group |
| Relative Risk Reduction | The percentage reduction in risk between the control and experimental groups |
| Number Needed to Treat (NNT) | The number of patients that need to be treated to prevent one additional event |
Example of Absolute Risk Reduction Calculator
Let’s consider an example to understand the ARR calculation better. Suppose we have a clinical trial with 200 subjects, where 100 are in the control group (n_c) and 100 are in the experimental group (n_e). In the control group, 20 patients experienced the event (CER = 0.20), while in the experimental group, 10 patients experienced the event (EER = 0.10).
Using the ARR formula:
ARR = (0.20 – 0.10) * ( (100 * 100) / (100 + 100) )
ARR = 0.10 * ( 10000 / 200 ) = 0.10 * 50 = 5
Thus, the Absolute Risk Reduction is 5 percent, indicating that the experimental treatment reduces the risk of the event by 5 percent compared to the control group.
Most Common FAQs
Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) measures the actual difference in event rates between the control and experimental groups. In contrast, Relative Risk Reduction (RRR) measures the percentage reduction in risk between the two groups. ARR provides a direct measure of the treatment’s effectiveness, while RRR offers a relative perspective.
The ARR calculator is used in clinical trials to determine the effectiveness of a new treatment or intervention. By comparing the event rates between the control and experimental groups, researchers can assess how much the treatment reduces the risk of the event. This information is critical for making informed decisions about the treatment’s efficacy and safety.
Understanding ARR is vital in medical decisions because it provides a clear and direct measure of how much a treatment reduces the risk of a negative outcome. This helps healthcare professionals and patients make informed choices about treatment options, considering both the benefits and potential risks.