The Cliff Jump Speed Calculator estimates the final speed of a jump from a cliff based on the height of the fall. By applying principles of physics, this tool provides an accurate measure of the speed at the moment of impact with the water or ground below. This information is particularly useful for assessing the safety and dynamics of cliff jumping.
Formula for Calculating Cliff Jump Speed
To calculate the final speed, assuming the jump starts from rest and air resistance is negligible, the formula is:
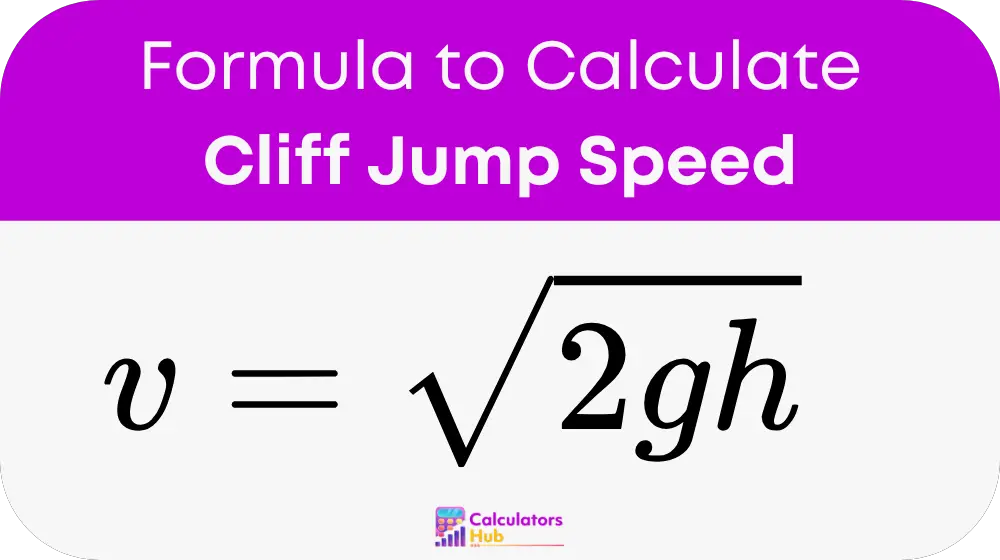
Where:
v is the final velocity in meters per second (m/s).
g is the acceleration due to gravity, approximately 9.81 m/s².
h is the height of the cliff in meters (m).
This formula relies on the principle of conservation of energy, where potential energy converts to kinetic energy during the fall.
Pre-Calculated Speeds for Common Heights
Here is a table for quick reference to common cliff heights and their corresponding speeds:
| Height (meters) | Final Speed (m/s) |
|---|---|
| 5 | 9.90 |
| 10 | 14.00 |
| 15 | 17.15 |
| 20 | 19.80 |
| 25 | 22.14 |
| 30 | 24.26 |
This table can help you estimate speed without recalculating for frequently encountered heights.
Example of Cliff Jump Speed Calculator
Imagine jumping from a cliff with a height of 20 meters. Using the formula:
v = √(2 × 9.81 × 20)
v ≈ 19.80 m/s
The final speed at the point of impact would be approximately 19.80 meters per second.
Most Common FAQs
The calculator measures the final velocity of a cliff jump based on the height of the fall. This velocity represents the speed at the moment of impact, helping to estimate safety and energy considerations.
No, it does not. The formula assumes ideal conditions without air resistance. In reality, air resistance slightly reduces the final speed, depending on factors like body position and wind.
Yes, the formula applies universally to any object in free fall under gravity, as long as air resistance is negligible. It’s suitable for physics experiments or other applications involving gravitational acceleration.