The Microscope Resolution Calculator is a tool design to calculate the resolution of a microscope given specific inputs. It simplifies the process, ensuring researchers and students can focus more on analysis and less on manual calculations.
Formula of Microscope Resolution Calculator
The resolution of a microscope can be effectively calculated using the formula:
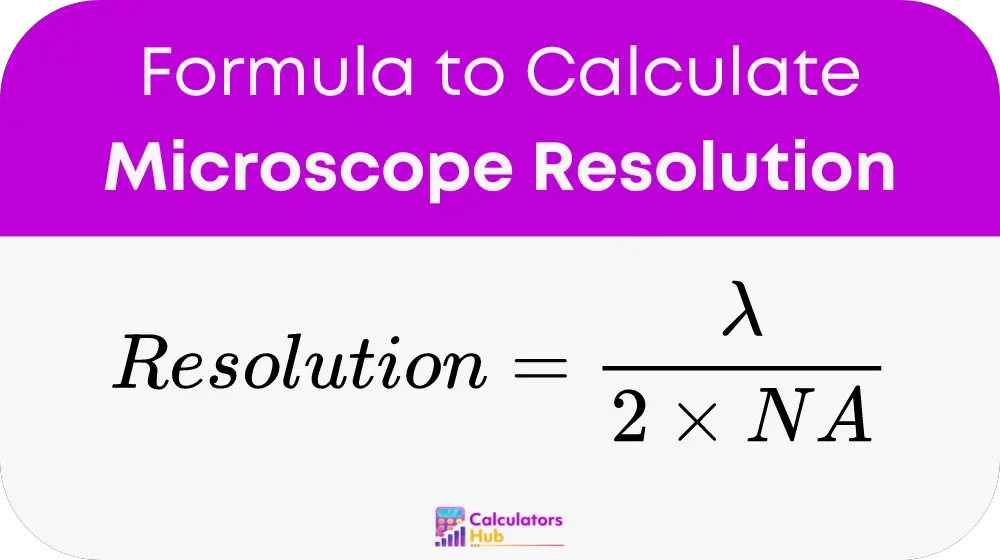
where lambda (λ) represents the wavelength of light used, and NA stands for Numerical Aperture, indicating the range of angles over which the system can collect or emit light. This formula is foundational in understanding how microscope settings can be optimized for clearer, more detailed images.
Practical Table for Quick Reference
To facilitate easy access to commonly needed resolution calculations, here is a table with predefined values:
| Lambda (nm) | NA | Resolution (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | 1.4 | 143 |
| 500 | 1.4 | 179 |
| 600 | 1.4 | 214 |
This table helps users apply the calculator more efficiently, providing a quick reference to common scenarios.
Example of Microscope Resolution Calculator
To clear the concepts further more let us look at an example.
Imagine you are using a microscope with a wavelength of 500 nm and a numerical aperture of 1.4. According to our calculator:
Resolution = 500 / (2 * 1.4) = 179 nm
This example shows how you can quickly determine the resolution necessary for your specific microscopy tasks.
Most Common FAQs
The shorter the wavelength, the better the resolution, assuming other factors are constant.
Higher NA values generally increase resolution as they allow the microscope to capture more light at wider angles.
This calculator is design for optical microscopes; electron microscopes typically require different calculations due to their use of electron beams instead of light.