The calculator simplifies the process of predicting the direction of shift in chemical equilibria due to changes in temperature, concentration, and pressure, making it a necessary tool for chemists.
Benefits of Using the Calculator
The calculator offers several advantages including efficiency, accuracy, and educational value, which are beneficial for students and professionals in the chemical industry.
Formula of Le Chatelier’s Principle Calculator
General Formula
The formula for the equilibrium constant is pivotal for understanding chemical reactions:
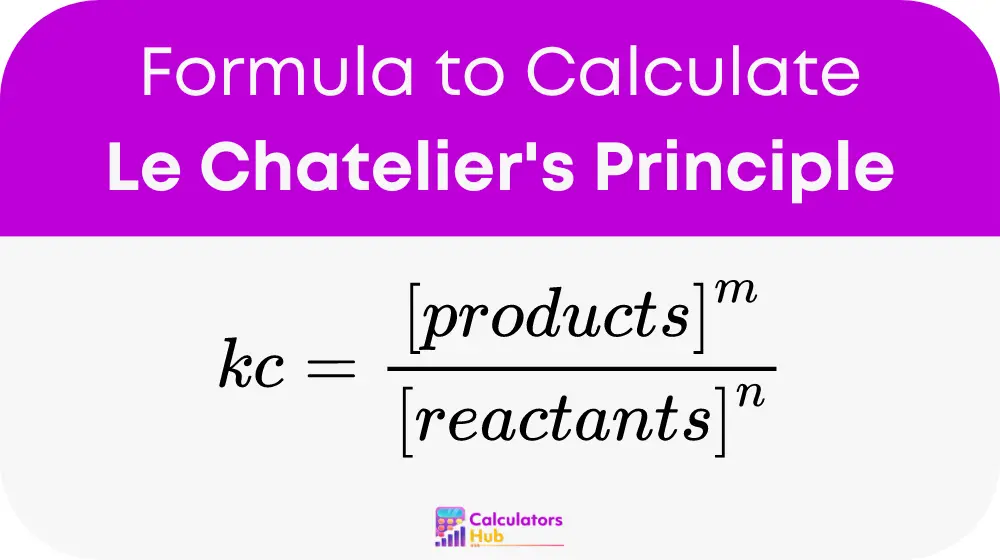
This formula helps calculate how concentrations will change in response to external conditions.
Application in the Calculator
This formula is essential for the calculator’s functionality as it provides quantitative answers to chemical equilibrium problems.
Helpful Tables for Quick Reference
Common Calculations
| Reaction | Initial Kc | Change | Final Kc |
|---|---|---|---|
| A + B ⇌ C + D | 1.00 | Increase Temp | 1.10 |
| E + F ⇌ G + H | 0.50 | Decrease [E] | 0.45 |
Conversion Factors
| Description | Conversion |
|---|---|
| Celsius to Kelvin | C + 273.15 = K |
| mol/L to ppm | mol/L x Molecular Weight x 1000 = ppm |
Example of Le Chatelier’s Principle Calculator
Demonstrating the Calculator
Use the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) at 300 K for a practical demonstration:
- Initial Setup: Input the balanced equation and initial conditions.
- Change Implementation: Increase the temperature to 350 K.
- Using the Calculator: Follow the steps for data input and execution.
- Interpreting Results: The output will indicate a shift towards the reactants, reducing NH3 production.
Most Common FAQs
Answer: The calculator can predict equilibrium shifts due to changes in concentration, pressure, and temperature.
Answer: The calculator is precise, validated against experimental data, and regularly updated to ensure reliability.
Answer: Discuss the availability of a mobile application and its functionalities, if applicable.