The Effective Number Of Species Calculator helps measure biodiversity in ecosystems by estimating how many equally common species would result in the same level of diversity as seen in a given sample. This method offers a more realistic picture of species distribution than a simple species count.
This tool falls under the Ecology & Biodiversity Calculators category. It is widely used by ecologists, conservationists, researchers, and environmental scientists to evaluate the richness and evenness of species in natural habitats.
By focusing on both abundance and evenness, the calculator translates the Shannon Diversity Index into a clearer number that’s easier to understand and compare across different ecosystems.
formula of Effective Number Of Species Calculator
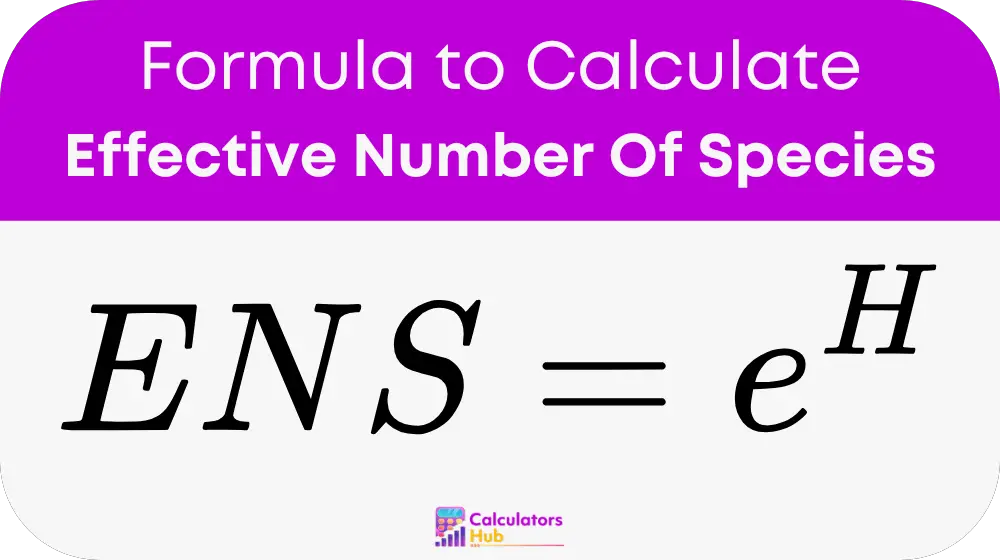
Variables:
- ENS:
Effective Number of Species — the true diversity value adjusted for evenness among species. - H:
Shannon Diversity Index — measures species diversity based on abundance and distribution. - p_i:
Proportion of individuals of species i in the entire sample (e.g., 20 out of 100 = 0.2). - e:
The natural base of the logarithm, approximately equal to 2.718.
Calculation Steps:
- Collect species data:
Count how many individuals belong to each species in the sample. - Find total individuals (N):
Add the number of individuals across all species. - Calculate proportions (p_i):
For each species:
p_i = number of individuals of species i / N - Find Shannon Index (H):
H = -Σ(p_i * ln(p_i)), where ln is the natural logarithm. - Calculate ENS:
ENS = e^H
This final value gives the number of equally abundant species that would produce the same diversity level as your sample.
Reference Table: Shannon Index vs. ENS
The following table helps you get an idea of how the Shannon Diversity Index translates into Effective Number of Species:
| Shannon Index (H) | ENS (e^H) |
|---|---|
| 0.00 | 1.00 |
| 0.69 | 2.00 |
| 1.10 | 3.00 |
| 1.39 | 4.00 |
| 1.61 | 5.00 |
| 2.00 | 7.39 |
| 2.30 | 10.00 |
Note: The ENS grows exponentially with H, so even small changes in H can lead to big changes in ENS.
Example of Effective Number Of Species Calculator
Scenario:
A sample from a forest includes the following counts:
- Species A: 40 individuals
- Species B: 30 individuals
- Species C: 20 individuals
- Species D: 10 individuals
Step 1: Total individuals (N) = 100
Step 2: Proportions:
p_A = 40 / 100 = 0.4
p_B = 30 / 100 = 0.3
p_C = 20 / 100 = 0.2
p_D = 10 / 100 = 0.1
Step 3: Shannon Index (H) =
= -[0.4 * ln(0.4) + 0.3 * ln(0.3) + 0.2 * ln(0.2) + 0.1 * ln(0.1)]
= -[(0.4 * -0.9163) + (0.3 * -1.2040) + (0.2 * -1.6094) + (0.1 * -2.3026)]
≈ -[-0.3665 – 0.3612 – 0.3219 – 0.2303]
≈ 1.2799
Step 4: ENS = e^1.2799 ≈ 3.60
Result:
Although four species are present, the effective number of species is about 3.6, showing that the species are not equally distributed.
Most Common FAQs
A: ENS considers both how many species there are and how evenly their populations are spread. Just counting ignores dominance by one or two species.
A: Yes. ENS is usually lower when one or two species dominate and others are rare. It equals the number of species only when all species are equally abundant.
A: The minimum is 1 (when one species dominates completely). The maximum equals the total number of species, but only if all species are equally common.