A Decays Per Minute (DPM) Calculator helps scientists, medical professionals, and researchers measure the rate of radioactive decay in a sample. This calculation is essential in nuclear physics, radiology, environmental monitoring, and medical imaging, where understanding the activity of radioactive materials is crucial.
DPM provides a measure of how many atoms in a substance undergo radioactive decay each minute. This information is useful for radiation safety, nuclear medicine, and radioisotope dating, ensuring that the handling and application of radioactive substances are precise and controlled.
Formula for Decays Per Minute Calculator
The Decays Per Minute (DPM) is calculated using the following formula:
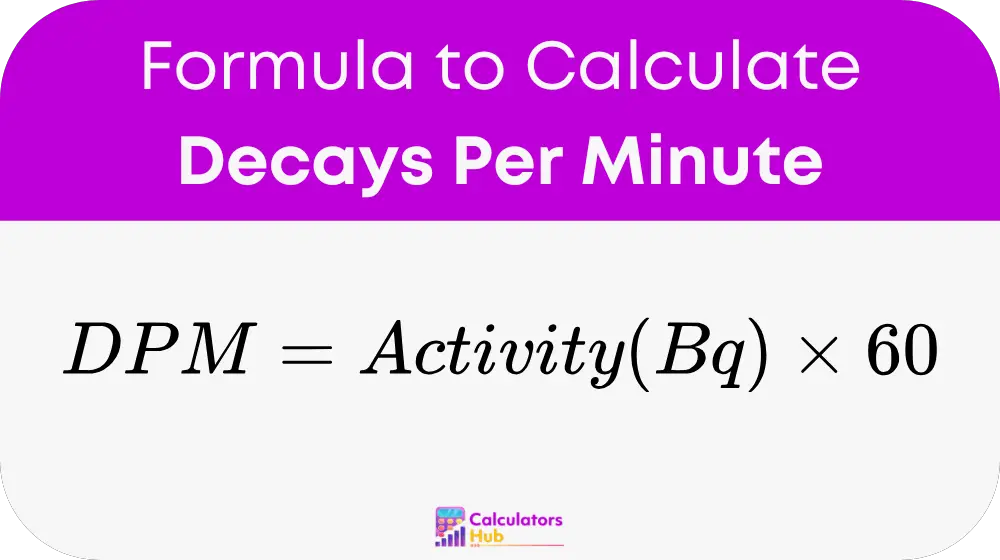
Where:
Activity (Bq) = Number of decays per second (measured in becquerels)
60 = Conversion factor from seconds to minutes
If the activity is given in curies (Ci), it must first be converted to becquerels:
Activity (Bq) = Activity (Ci) × 3.7 × 10¹⁰
Then apply the formula:
DPM = (Activity in Bq) × 60
This formula allows users to quickly determine the decay rate of a radioactive substance over time, which is important for applications in radiation therapy, nuclear power, and laboratory research.
Decays Per Minute Reference Table
To simplify radioactive decay calculations, the following table provides estimated DPM values for different activity levels.
| Activity (Bq) | Activity (Ci) | Decays Per Minute (DPM) | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Bq | 2.7 × 10⁻¹¹ | 60 | Background radiation |
| 100 Bq | 2.7 × 10⁻⁹ | 6,000 | Environmental monitoring |
| 1,000 Bq | 2.7 × 10⁻⁸ | 60,000 | Low-level radioactive waste |
| 1 μCi | 3.7 × 10⁴ | 2.22 × 10⁶ | Nuclear medicine |
| 1 mCi | 3.7 × 10⁷ | 2.22 × 10⁹ | Radiation therapy |
This table serves as a quick reference for scientists and medical professionals who need to estimate decay rates in different measurement units.
Example of Decays Per Minute Calculator
A radioactive sample has an activity of 500 Bq, and a scientist wants to calculate the decays per minute (DPM).
Step 1: Apply the DPM Formula
DPM = Activity (Bq) × 60
DPM = 500 × 60
Step 2: Compute the Result
DPM = 30,000 decays per minute
This means that the radioactive sample undergoes 30,000 decays every minute, which is crucial information for radiation exposure assessments and medical applications.
Most Common FAQs
Becquerels (Bq) measure the number of radioactive decays per second, while curies (Ci) are a larger unit use in nuclear physics and medicine. One curie equals 3.7 × 10¹⁰ becquerels, meaning curies represent much higher activity levels.
DPM helps determine the intensity of radiation exposure from a source. It is use in radiation safety protocols to assess the risk of exposure and to ensure safe handling of radioactive materials in medical, industrial, and environmental settings.
Yes, DPM is a fundamental metric in radiation exposure calculations. By knowing the decay rate and energy emitted, radiation dosimetry experts can estimate the dose received by individuals working with radioactive substances.