The MC Delta T Calculator is a specialized tool designed to calculate the change in temperature (ΔT) of a substance when it undergoes heat transfer. This calculator is invaluable for students, engineers, and scientists alike, providing quick and accurate results that are crucial for experiments and industrial applications.
Formula of MC Delta T Calculator
At the heart of the calculator is the formula:
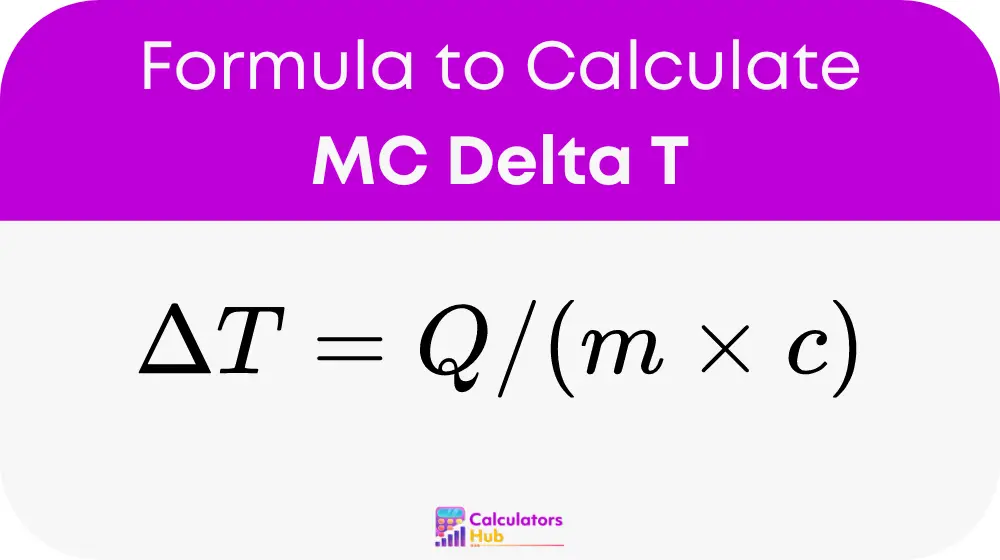
where:
- ΔT is the change in temperature,
- Q is the heat transferred to or from the substance,
- m is the mass of the substance, and
- c is the specific heat capacity of the substance.
This formula is fundamental in thermodynamics, the study of heat transfer, and energy conversion.
Useful Conversions Table
To enhance the utility of the MC Delta T Calculator, here is a table with common substances and their specific heat capacities, along with typical conversion factors:
| Substance | Specific Heat Capacity (J/g°C) | Common Conversions |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 4.18 | 1 liter = 1 kg |
| Iron | 0.45 | |
| Copper | 0.39 |
This table ensures users have the necessary data at a glance, facilitating quicker calculations.
Example of MC Delta T Calculator
Let’s calculate the change in temperature for 2 kg of water absorbing 5000 Joules of heat. Using the formula:
- ΔT = 5000 / (2 * 4.18)
- ΔT = 5000 / 8.36 ≈ 598.56°C
This example demonstrates the straightforward nature of using the MC ΔT Calculator.
Most Common FAQs
It’s the amount of heat per unit mass required to raise the temperature by one degree Celsius.
Use a calibrated scale or balance to ensure precision in your calculations.
Yes, as long as you know the substance’s specific heat capacity and other relevant variables.